Follow Up Questions from Chapter 13: Natural Polymers Natural Latex Rubber Cellulose
advertisement

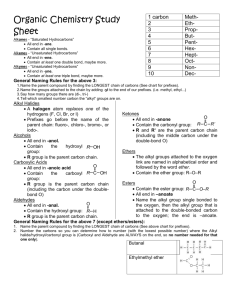
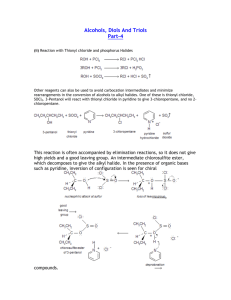
Follow Up Questions from Chapter 13: Natural Polymers Natural precursor Natural Latex Rubber Industrial precursor Cellulose Spider Silk CHAPTER 14 Oxygen, Halogens, & Sulfur General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 14: Oxygen, Halogen, & Sulfur Learning Objectives: Name organic compounds with carbon-heteroatom single bonds (oxygen, halogens, sulfur) Identify 1°, 2°, 3° alcohols and alkyl halides Predict the products or reactants for following reactions: Alcohol dehydration Alcohol oxidation Sulfur oxidation Sulfur reduction 3 Smith. General Organic & Biolocial Chemistry 2nd Ed. Functional Groups Overview Alkyl halides Single Bond to a Heteroatom Functional Groups Alcohols Ethers Thiols 4 Smith. General Organic & Biolocial Chemistry 2nd Ed. Alcohols & Alkyl Halides 1°, 2°, 3° Alcohols Nomenclature # 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 OH 1 prefix + prefix 6 4 2 3 5 parent + suffix Greek Straight Chain Root Alkane Name methane meth ethane eth propane prop butane but pentane pent hexane hex heptane hept octane oct nonane non decane dec First give location and type of substituents Second give location of double bond parent How many carbons in longest chain? suffix How many of the functional group and what is it? Alcohol = “ol” 2-methyl 4- hexan ol # Carbons 1 2 3 4 5 6 Alkyl Group Structure Name CH3methyl CH3CH2ethyl CH3CH2CH2propyl CH3CH2CH2CH2butyl CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2pentyl CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2hexyl *Note: after the greek root of the parent use “an”, ie hexan * Second Note: when we have more then 1 multiple bond the parent name has an “a” after the greek root: hexa 6 Smith. General Organic & Biolocial Chemistry 2nd Ed. Functional Groups Alcohols Fermentation 7 Smith. General Organic & Biolocial Chemistry 2nd Ed. Rxns of Alcohols Elimination Reaction: Dehydration Zaitsev Rule: The major product in elimination is the alkene that has more alkyl groups bonded to it. Rxns of Alcohols Oxidations Oxidation requires breaking C-H bonds and forming new C-O bonds. When alcohol is the starting material the products always have a carbonyl group. Rxns of Alcohols Alcohol Metabolism Find notes from arthur’s explaination Ethers Nomenclature # 1 O prefix + prefix 4 2 parent + 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 3 suffix Use alkyl substitutant naming roots, but drop the “yl” and use “oxy” for the simplest alkyl group bonded to the ether oxygen. parent How many carbons in longest chain? suffix Use alkane ending: ane 2-ethoxy but ane # Carbons 1 2 3 4 5 6 Greek Straight Chain Root Alkane Name methane meth ethane eth propane prop butane but pentane pent hexane hex heptane hept octane oct nonane non decane dec Alkyl Group Structure Name CH3methyl CH3CH2ethyl CH3CH2CH2propyl CH3CH2CH2CH2butyl CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2pentyl CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2hexyl 11 Smith. General Organic & Biolocial Chemistry 2nd Ed. Functional Groups Ethers Diethyl Ether The first anesthetic administered in 1842 by Crawford Long Heterocycles O 12 Smith. General Organic & Biolocial Chemistry 2nd Ed. Thiols Nomenclature # 5 3 prefix + parent + prefix SH 2 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 suffix Greek Straight Chain Root Alkane Name methane meth ethane eth propane prop butane but pentane pent hexane hex heptane hept octane oct nonane non decane dec Give location and type of substituents, then give location of thiol group. parent How many carbons in longest chain? suffix Hydrocarbon functional group suffix + “thiol” 2,4-dimethyl 1- hept anethiol # Carbons 1 2 3 4 5 6 Alkyl Group Structure Name CH3methyl CH3CH2ethyl CH3CH2CH2propyl CH3CH2CH2CH2butyl CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2pentyl CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2hexyl 13 Smith. General Organic & Biolocial Chemistry 2nd Ed. Functional Groups Thiols Insulin Jean-Philippe Cartailler, Ph.D. The Beta Cell Consortium Smith. General Organic & Biolocial Chemistry 2nd Ed. 14 Rxns of Thiols Oxidation & Reduction Alkyl Halides Nomenclature # 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 2 6 4 Cl prefix + prefix 3 5 parent + suffix Give location and type of substituents. Replace “ine” in halide name with “o”, ie Chlorine = chloro parent How many carbons in longest chain? suffix What is the hydrocarbon functional group? If alkane then “ane” suffix 2-chloro 4-methyl hex ane # Carbons 1 2 3 4 5 6 Greek Straight Chain Root Alkane Name methane meth ethane eth propane prop butane but pentane pent hexane hex heptane hept octane oct nonane non decane dec Alkyl Group Structure Name CH3methyl CH3CH2ethyl CH3CH2CH2propyl CH3CH2CH2CH2butyl CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2pentyl CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2hexyl 16 Smith. General Organic & Biolocial Chemistry 2nd Ed. Functional Groups Alkyl Halides Rxns of Alkyl Halides Substitution Reactions with Alkyl Halides Substitution Reactions at 1° Carbons Halides (Cl, Br) are good leaving groups (L) because they form very polar covalent bonds with carbon. Nucleophiles (Nu-) include negatively charged molecules or amines (RNH2). Common Nucleophiles: NaOH ( OH-), NH3, RS-, I-. Rxns of Alkyl Halides Substitution Reactions Substitution Reactions at 1° Carbons Substitution Reactions at 3° Carbons Rxns of Alkyl Halides Substitution Reactions