Histology What to look for
advertisement

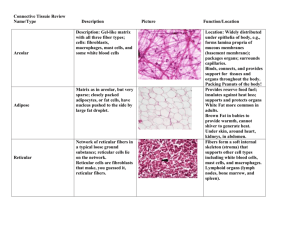
Histology What to look for Histology review Histology Practical = 50 pts • Some slides set up on scopes (~10) • Some Powerpoint pictures on the projector Questions I will ask: • What kind of tissue? • General function? (e.g. absorption, protection) • What cells, fibers, ground? • An example of where would you find it? Slides • Epithelial tissues (7 types, could be ANY of the examples provides) • Connective tissues (11 types, ANY example that we looked at) • Muscles (3 types) or neruons • Integument and accessory structures Epithelial tissue Simple cuboidal epithelium • Lining kidney tubule • Large, spherical, usually central nucleus Another example - kidney Simple squamous Simple squamous • Really flat cell layer. • Cytoplasm very thin, visible only at point of central nucleus Kidney Superficial view (squamous) Simple columnar Intestinal lining Oblong nuclei which may be much closer to one side than the other Simple columnar Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium • Trachea • Look like multiple layers • ciliated Figure 4–5b Another example Transitional Epithelium • Urinary bladder • Looks stratified, with no coherent layers and dome shaped cells at the top Figure 4–4c Transitional Stratified Squamous Epithelium • Skin • Many layers thick, flat cells at top Figure 4–3b Stratified squamous Stratified squamous Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium • Sweat gland ducts • Two layers with large spherical nuclei Figure 4–4b Stratified Columnar Epithelium • Salivary gland duct • Only top layer lining lumen looks columnar Figure 4–5c Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue proper • Loose connective tissue – Areolar – Adipose – Reticular • Dense connective tissue – Dense regular – Dense irregular – Elastic tissue Fluid CT –Blood Supporting CTs •Cartilage –Hyaline cartilage –Elastic cartilage –Fibrocartilage • Bone Areolar tissue • A loose CTP Areolar Areolar: what to look for • • • • Fibroblasts Collagen fibers Elastic fibers Mast cells and macrophages • Found? Throughout body, under dermis, divides skin from underlying tissues Adipose tissue • Another lose CTP (note nucleus) Adipose: what to look for • Lots of cytoplasm • Slim nuclei pushed off the side • Found? You know where Reticular tissue • The third type of loose CTP Reticular: what to look for • Reticular fibers (network) • Found? Internal framework in many sort organs (liver, spleen) supporting the parenchyma Dense regular Dense regular: what to look for • • • • Thick parallel bundles of collagen Thick fibers Little space in between fibers Small fibroblast nuclei in between bundles • Found? Tendons, ligaments, deep fascia. Dense irregular More dense irregular Dense irregular: what to look for • Mesh of collagen fibers (irregular looking) • Interspersed fibroblasts • Found? Dermis of skin, periosteum, perichondrium Elastic tissue Elastic tissue Elastic tissue: what to look for • Elastic fibers (instead of collagen fibers) in large bundles • Smaller width fibers • More space in between fibers • Fibroblast nuclei (sometimes visible) • Found? Between vertebrae, in blood vessel walls (underneath endothelium) Fluid CT • Blood Blood: what to look for • RBCs • White blood cells (darker): monocytes, lymphocytes, granulocytes • Platelets Supportive CT • Cartilage – gelatinous, padding – Hyaline cartilage – Elastic cartilage – Fibrocartilage Hyaline cartilage • Glasslike because fibers not visible More hyaline • There are collagenous and elastic fibers lying in the cartilage matrix but they are invisible because their “refractive index” is the same as that of the matrix (like cornea) Hyaline cartilage Hyaline • Hyaline cartilage (lavender matrix), with perichondrium (pink) outside it. The latter is a dense regular collagenous CT. Cartilage cells = chondrocytes, and they are lying in the lacunae. Hyaline cart.: what to look for • Perichondrium • Chondroblasts (make the matrix fibers and ground) • Chondrocytes and lacunae • Where? Most joints, nasal septum Elastic cartilage Elastic cartilage Elastic cart: what to look for • Many elastic fibers in matrix (or sometimes to the sides) • Chondrocytes in lacunae, often stacked up like a totem pole • Found? External ear Fibrocartilage Fibrocartilage: what to look for • Irregular, wispy collagen fibers • Chondrocytes in lacuna • Found? Intervertabral discs of spine, pads in knee joint Supportive CT: Bone Bone: what to look for • • • • • • Osteon (whole circular structure) Concentric lamellae (of matrix) Central canal (at center of lamellae) Osteoblasts Osteocytes in lacunae Canaliculi Found? Bones! Nervous Tissue Figure 4.10 Nervous Tissue Figure 4.10 Nervous tissue: what to look for • Large, pyramidal cell bodies • Long processes extending out • Space (it’s a smear so cells don’t usually take up the whole area) • Found? Nerves, CNS 3 Types of Muscle Tissue • Skeletal muscle: – large body muscles responsible for movement • Cardiac muscle: – found only in the heart • Smooth muscle: – found in walls of hollow, contracting organs (blood vessels; urinary bladder; respiratory, digestive and reproductive tracts) Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Figure 4.11a Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Figure 4.11a Skeletal Muscle: what to look for • Long, cylindrical cells with obvious striations (stripes) • Multinucleate cells with the nuclei at the periphery (not in the center) Muscle Tissue: Cardiac Figure 4.11b Cardiac Muscle Cardiac Muscle: what to look for • Branching, striated cells interlocking at intercalated discs • Uninucleate cells Muscle Tissue: Smooth Figure 4.11c Muscle Tissue: Smooth Figure 4.11c Muscle Tissue: Smooth • Sheets of spindle-shaped cells with no striations • Central nuclei Integument Epidermis and dermis Epidermis What to look for: • Usually darkest between stratum germinativum and stratum granulosm (granulosm often a dark meandering line) • Keratinized cells often lift off the section • Melanocytes just below basal lamina Dermis: Papillary vs. Reticular layer What to look for: • Papillary layer – has ridges – is areolar – Just under basal lamina • Reticular layer – much thicker – Dense irregular CT Again Merocrine sweat gland • What to look for: – Found in most skin – Coiled, tubular – Small lumens in cross section – Have duct that goes all the way to the epidermal surface and ends in sweat pore – Smaller than apocrine, don’t extend as deep into dermis Apocrine sweat gland Apocrine sweat gland What to look for: • Associated with hair follicle • Only in nipples, groin, armpit • Large lumens • Deeper in dermis than merocrine Hair with sebaceous glands and arrector pilli Hair What to look for: • Follicles are rarely complete • Can often see root, papilla (at base, wher hair grows) • Arrector pilli muscle at an angle • Associated glands (which are?) Sebaceous glands Sebaceous glands What to look for: • Associated with hair follicle • Found most everywhere hair follicles are found in skin • Look like cauliflower (maybe?) Sebaceous follicle Sebaceous follicle What to look for: • Also look like cauliflower • Found on face and trunk only • NOT associated with hair follicle • Have duct that opens onto skin surface Random Examples Can you figure them out?