Building Blocks Carbo-
advertisement

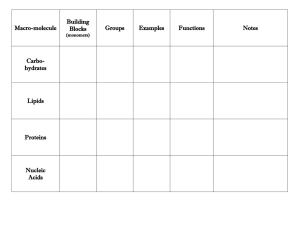
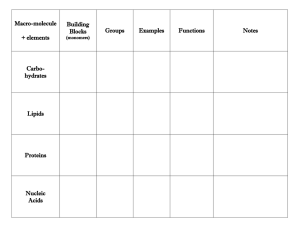
Macro-molecule Building Blocks (monomers) Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Groups Examples Functions Notes Macro-molecule Building Blocks Groups Examples Functions Notes (monomers) mono-: glucose fructose galactose Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins monosaccharides (simple sugars) 3 fatty acids + glycerol (3C) monodipolysaccharides poly-: starch, cellulose, glycogen chiton triglycerides (simple lipids) phospholipids cholesterol amino acids deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) Nucleic Acids nucleotides: phosphate, sugar, nitrogen base di-: sucrose maltose lactose ribonucleic acid (RNA) adenosine triphophate (ATP) mono-, di-: Energy source poly-: starch: food storage-plants cellulose: plant support glycogen: food storage-animals chiton: exoskelton nutrition cell membrane cholesterol derivatives like hormones sucrase enzymatic transmembrane transport, relay insulin messengers antibodies immunity muscles, hair, skin, fingernails structural control of the cell, heredity messenger (mRNA) organizer (rRNA) translator(tRNA) energy shuttle bond: or glycosidic linkage between sugar monomers. linkages between monomers in starch, linkages in cellulose. Enzymes specific for catalyzing the breakdown of linkages are ineffective on linkages. Humans cannot digest wood or the fibers in celery or whole grain. This fiber acts as “roughage” stimulating the intestine to secrete mucus to promote regular bowel movements. bond: ester linkage between each fatty acid and the glycerol. bond: peptide bond between carboxyl and amino group of 2 amino acids. bond: phosphodiester between phosphate and sugar Bacterial DNA has a main chromosome plus circular DNA called plasmids 10 nucleotides per turn A=T(U); C=G