002b Biological Molecules
advertisement

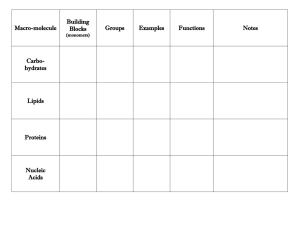
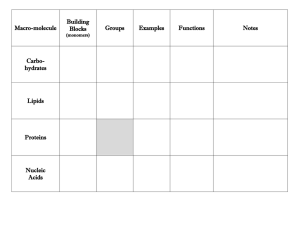
Introduction to important molecules which comprise the structure and function of all living organisms Biological Compounds Categories: Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids • Principle Elements • Ratio of Various Elements • Special Functional Groups Hydroxyl ( -OH ) O H Alcohols Carbonyl (C=O) C O Aldehydes, Ketones Carboxyl ( -COOH ) C Carboxylic acids O Amino ( -NH2 ) N H Amines Phosphate ( -H2PO4) O P Sulfhydryl ( -SH) S H Organic phosphates Thiols Monomer • Subunits that serve as building blocks • Connected by condensation reactions (dehydration) Polymers • Covalent bonding occurs • Solubility in Water Monomer Polymer Monomers H HO H HO H2O Polymer C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 C12H22O11 + H2O H2O Monomers H2O H HO C12H22O11 + H2O C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 Principle Elements: C, H, & O H:O = 2:1 Many Hydroxyl Groups (-OH) Monomers: Monosaccharides Polymers: Polysaccharides Water Soluble • • • • Energy Metabolism Structural Components Cell-to-Cell Contacts and Recognition Elimination of wastes (fiber) APT cell HelperT cell Chemical Formulas C6H12O6 From corn syrup C6H12O6 Chemical Formulas C5H10O5 C5H10O4 deoxyribose Lactose glucose + galactose Maltose Sucrose glucose + glucose glucose + fructose glycogen Starch vs. Cellulose Corn starch Potato starch Starch vs. Cellulose We can digest starch (amylose) but not cellulose. What difference do you see that might be the reason behind this? Digest Cellulose cecum Trichonympha, protist found in termites guts • Principle Elements: C, H, & O • Some With P & N • H:O >>> 2:1 • Diverse Group of Biological Molecules • Water Insoluble • Energy Storage • Protection & Cushioning of Body Organs • Structural Components of Membranes • Chemical Messengers (hormones) • • • • • Triglycerides (neutral fats) Phospholipids Sterols Waxes Vitamins (D, E, K) Glycerol Fatty Acid • Saturated with H+ • Most animal fats are saturated, ex. butter • Solid at room temp Glycerol Fatty Acids • Has one or more double bonds between carbons • Most vegetable fats • Liquid at room temp carbon hydrogen phosphorous oxygen Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tails Nonpolar hydrophobic tails (fatty acids) exposed to oil Polar hydrophilic heads exposed to water Bacon grease cholesterol • • • • • Cholesterol: < 175 mg/dl Triglycerides: 30-175 mg/dl HDL: >35 LDL: <130 Cholesterol/HDL ratio: <4.5 indicates heart disease • • • • • • Family history of vascular disease High levels of blood cholesterol Smoking Diabetes Hypertension Obesity • • • • • • • Eat healthy Exercise Lose wt. Quit smoking 1 glass wine or beer Medication Surgery • Principle Elements: C, H, O, & N • Monomers: Amino Acids • Polymers: Polypeptides or Proteins • Generally Water Soluble Functional Groups of Amino Acids • Carboxylic Acid (-COOH) • Amine (-NH2) • R-Groups (variable - 20 different kinds) • Enzymes • Structural Proteins • Chemical Messengers (Hormones) • Contractile • Antibodies Amino Acid carboxyl amine Functional R 20 Known Amino Acids Amino Acid Protein Valine Histadine Leucine Threonine Proline Cystine Serline Proline Glutamic Acid Glutamic Theronine Valine Acid hemoglobin keratin Protein Structures Proteins can denature Heat Pressure pH Protein Bond Types 1.Peptide bond 2.Hydrogen bond 3.Salt (ionic) bond 4.Disulfide bond Protein Bond Types AA1 AA2 Peptidebond bond Peptide Dipeptide Water Protein Bond Types Hydrogen bond Protein Bond Types Disulfide bond • Strong, chemical side bond • Cannot be broken by water • Can be broken by chemical hair relaxers • Alters the shape of the hair Protein Bond Types Salt (Ionic) bond Attraction of unlike charges Negative charge in an amino acid attracts the positive charge in another amino acid grouping • Catalysts- speed up a reaction • Not used up by reaction • Decrease activation energy of a reaction (activation energy is needed to break chemical bonds) Enzymatic reactions are affected by: Temperature pH Substrate conc. Enzyme conc. Are very specific for their substrate Substrates: Bind only to a restricted region of the enzyme (active site) Held in place by weak interactions (H-bonds) Active site Enzyme (sucrase) Specificity of enzyme: Lock and key Substrate (sucrose) The Functioning of Enzymes active site Enzyme Principle Elements: C, H, O, N, & P Monomers: Nucleotides Polymers: Nucleic Acids Generally Water Soluble Nucleotide Components: Ribose (5-C) Sugar Phosphate Nitrogenous Base • Genetic Instruction Set (DNA) • Protein Synthesis (DNA & RNA) • Energy Metabolism (ATP) Polymers made up of individual nucleotides Nucleotides contain • Phosphate group • Five carbon sugar • Ring shaped nitrogen base DNA contains information for almost all cell activities ATP Role of ATP in Energy Metabolism ATP ADP + Pi + Energy Role of ATP in Energy Metabolism INQUIRY 1. Describe the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats. 2. Where are phospholipids found? 3. Cholesterol is the base molecule for what type of lipids? 4. Name a polysaccharide used to store energy. 5. Name the currency molecule for all the cells activities.