Carbon and Macromolecules
advertisement

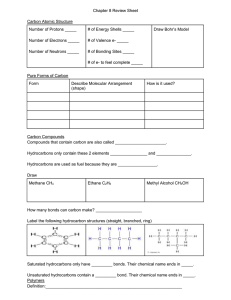
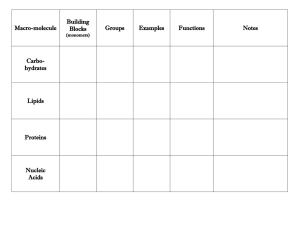
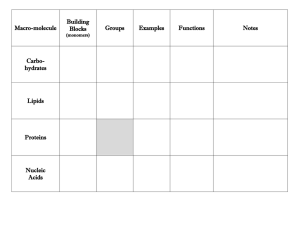
Carbon and Macromolecules Notes Organic Chemistry: Study of Carbon Containing Molecules ORGANIC is derived from ORGANISM because all living things are made up of carbon based compounds Simplest Organic Compounds: Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons are made up of ONLY Hydrogen and Carbon Simplest Hydrocarbon: Methane: CH4 Hydrocarbons are the result of Carbon having four unpaired valence electrons Therefore, Carbon prefers to bond with four other atoms/compounds This results in a large variety of compounds from methane to complex carbohydrates. Other Common Hydrocarbon Compounds: o Propane o Butane o Octane (Gasoline Pump) Other Molecules with Carbon: Macromolecules Carbohydrates: Contain sugars of the skeletal formula CH2O (example: Glucose is C6H12O6). Lipids: Contain Glycerol and Fatty Acids (Which are hydrocarbons) Proteins: Contain a Central Carbon surrounded by COOH, NH2, H and R Group Nucleic Acids: Contain a Sugar with Carbon surrounded by a Phosphate Group and a Nitrogen Base Carbohydrates: Monomers: Simple Sugars: Glucose, Fructose, Galactose, and Lactose Examples: Starch, Glycogen (Animal Cell), Starch/Cellulose (Plant Cell) Function in the Cell: Energy Storage, Support, CellCell Interactions Lipids: Monomers: Glycerol and Fatty Acids Examples: Butter, Fat, Peanut Butter, Oils Function in the Cell: Energy Storage, Insulation, Protection Proteins: Monomers: Amino Acids Bond linking monomers: Peptide Examples: Enzymes (specific proteins to speed up biological reactions), Hemoglobin (Helps transport oxygen to the blood Function in the Cell: Structural Support for Tissues and Cells, Aid in Metabolism Nucleic Acids: Monomers: Nucleotides (Sugar, Phosphate, Nitrogen Base) Bond linking monomers: Sugar-Phosphate and Hydrogen (between bases) Examples: DNA and RNA Function in the Cell: Genetic Code