Chapter 27 Test Study Guide 1. 2.
advertisement

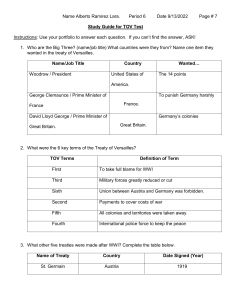
Chapter 27 Test Study Guide 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. The most “fatal decision” made by Tsar Nicholas II before the Russian Revolution (905) Grigori Rasputin (905) Cause of growing tension between Britain and Germany (890-891) Three Emperors’ League (889) The spark that ignited the Balkan “powder keg” in 1914 (892-893) The Battle of the Marne (895) Cause of Britain’s entry into the war (894) Order of events. What happened first (889) The Central Powers (898) The Petrograd Soviet’s Army Order No. 1 (906) The overall effect of WWI on European women (901) Walter Rathenau (900) Order of events. What happened last (889) “Splendid Isolation” (890) Lenin’s contribution to Marxist theory (906) The First Balkan War (892) Bismarck’s alliance system (888-889) The War Raw Materials Board in Germany (900) The Battles of Tannenberg and Masurian Lakes (895) Areas in the Balkans that were occupied by the Central Powers (898) European governments and total war (900-902, 904) Why Austria-Hungary chose war in July 1914 (892-893) The social impact of total war (901) The African colonial subjects of Britain and France (897) The offensives on the Western Front (895) Germany’s Auxiliary Service Law (900) Georges Clemenceau at the Paris Peace Conference (913) Iraq, Palestine, Transjordan, and Syria at the Paris Peace Conference (914) The harshness of the Treaty of Versailles on Germany (914) British Prime Minister Lloyd George’s electoral victory in December 1918 (912) Nicholas II’s failure in Russia politics (904) Alexander Kerensky (906) Bolsheviks were also known as (908) Social distinctions during the war (901) The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (909) The revolution in Austria-Hungry after WWI (911) The Cheka (910) Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War (910) The U.S’s rejection of The Treaty of Versailles (915) The Versailles settlement (912-914)