8. Carbs PPT
advertisement

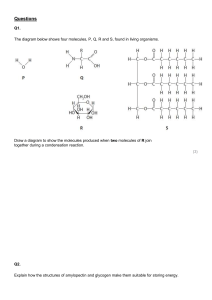
Organic Molecules Organic Compounds Contain C and H Often form long chains of carbon atoms linked by covalent bonds Macromolecules = large organic molecules abundant in living organisms Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Adenosine triphospate (ATP) Who studies macromolecules? Biochemistry is the study of the chemical interactions of living things Elements in Living Organisms Hydrogen (H) Oxygen (O) Carbon (C) Nitrogen (N) Phosphorus (P) Sulfur (S) Also the most abundant in macromolecules Macromolecule #1: Carbohydrates C, H, O (ratio 1:2:1) Purpose: energy and structure Three types: Monosaccharides (one sugar ring) Dissaccharides (two sugar rings) Polysaccharides (many sugar rings) Monosaccharides Quick energy Glucose = most important “fuel” in our body Fructose, galactose Disaccharides Short term energy storage Sucrose (table sugar) = glucose + fructose Lactose = glucose + galactose Polysaccharides Glycogen = energy storage; found in liver and muscles Starch = provides energy; the most consumed carbohydrate in human diet Cellulose = structural support; found in plants; humans cannot digest it (fiber) Glycogen Cellulose Formation and breakdown of macromolecules fig. 2.10 seen in digestion