Cell Membrane
advertisement
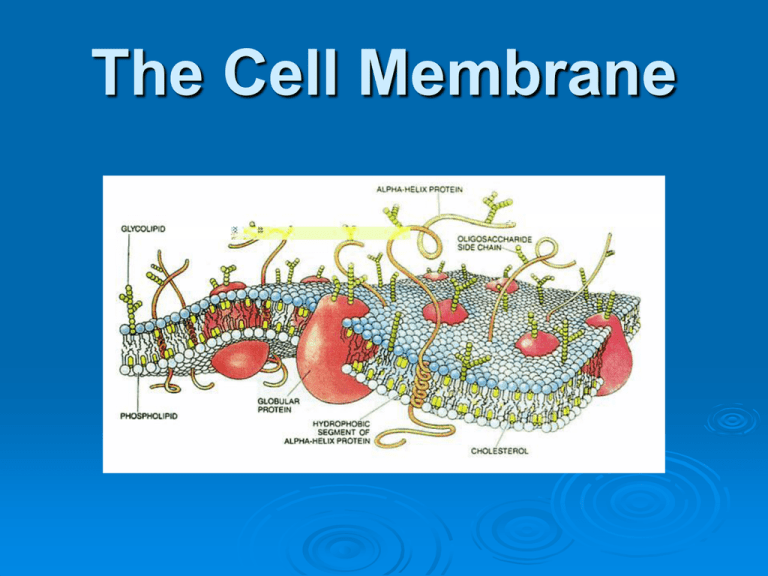
The Cell Membrane What is a membrane? A membrane is a device that selectively permits the separation of one or more materials from a liquid or gas. ? Passive Transport The transport of substances through the cell membrane without using energy. Now there are two different ways to transport material through the cell membrane WITHOUT using energy: Diffusion and Osmosis Diffusion The process of moving from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration Diffusion Demonstration Model Molecules are always in motion In a closed system the molecules evenly try to distribute Which results in a the initial movement of molecules from high to low concentrations Once an equilibrium is reached there is no net movement of molecule. What is separating the two different types of beads? How do the two volumes compare in this model? Which side of the model has a higher concentration of beads? How is diffusion going to take place? What happens with continued shaking? Is equilibrium reached? (Has homeostasis been reached?) Add: Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable internal environment. Dialysis It’s a process that separates solvents from blood. Such as removing glucose or fats with out removing the important molecules that our blood needs. The tubing used in semi-permeable. Meaning some material can pass through and other cannot. Osmosis Osmosis The diffusion of water from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration through a semipermeable membrane. Water moves from a high concentration of water (less salt or sugar dissolved in it) to a low concentration of water (more salt or sugar dissolved in it). This means that water would cross a selectively permeable membrane from a dilute solution (less dissolved in it) to a concentrated solution (more dissolved in it). Water can cross the cell membrane through the lipid bi-layer and with special proteins. If enough water enters the cell by osmosis, the cell can swell enough to burst open and die. This is demonstrated in the picture. In this picture a red blood cell is put in a glass of distilled water (all water with no salt or sugar in it). Because there is a higher concentration of water outside the cell, water enters the cell by OSMOSIS. In this case too much water enters and the cell swells to the point of bursting open. In the end pieces of cell membrane are left in the water. Osmosis Cont. The concentration (amount) of all substances affects the movement of materials in and out of the cell. Hypotonic Solute concentration: contains a low concentration of solute Water concentration: contains a high concentration of water Water movement: water diffuses into the cell Effect on the cell: causing the cell to swell and possible explode Cells in hypotonic solution Draw a picture Isotonic Solute concentration: is equal to the water concentration Water concentration: is equal to the solute concentration Water movement: equal diffusion (water diffuses into and out of the cell at equal rate) Effect on cell: none Normal cells in isotonic solution Draw a picture of an isotonic solution next to the definition Hypertonic Solute concentration: contains a high concentration of solute Water concentration: contains a low concentration of water Water movement: water diffuses out of the cell Effect on the cell: causing the cell to shrivel Cells in hypertonic solution Draw a picture next to the definition Quiz yourself 1 2 3 Active transport Active transport The transport of molecules from areas of high to low concentration with the use of energy. The cell energy is the ATP made in the mitochondria. Bulk movement of substances across the membrane Endocytosis: Phagocytosis Pinocytosis Exocytosis Endocytosis A process by which a cell surrounds and takes in materials from its environment by engulfing them. Phagocytosis Process in which phagocytes engulf and digest microorganisms and cellular debris "phagocyte" or eating cell (phago = "eating", cyte = "cell"). An important defense against infection Pinocytosis process by which certain cells can engulf and incorporate droplets of fluid Exocytosis when transport is out of the cell.








