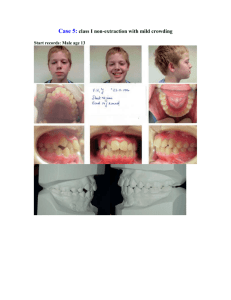
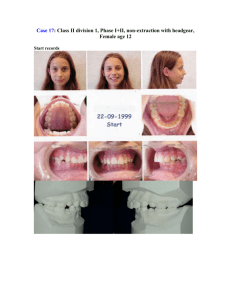
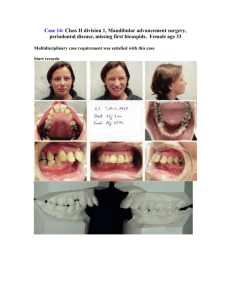
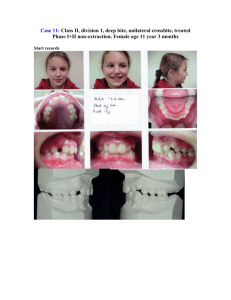
Lecture 11 cephalmetric analysis
advertisement
CEPHALOMETRY DR. ZUBER AHAMED NAQVI OBJECTIVES Steiner’s analysis- skeletal dental Soft tissue Tweed analysis Wits appraisal STEINER’S ANALYSIS He proposed the appraisal of various parts of skull separatelySkeletal Dental and Soft tissues Skeletal analysis relates upper and lower jaws to the skull and to each other. Dental analysis relates the upper and lower incisor teeth to their respective jaws and to each other. Soft tissue analysis assess the balance and harmony of the lower facial face. STEINER’S ANALYSIS • • • • • Skeletal analysis SNA Angle- SN plane and a line joining N to A. Average value-82 0 Increased –protrusive maxilla. Decreased – recessive maxilla • SNB angle- SN plane and a line joining N to B. • Average value-80 0 • Increased –protrusive mandible. • Decreased – recessive mandible • ANB angle- angle between lines joining nasion to point A and nasion to point B. • Average value- 2 0 • Increased –skeletal class II malocclusion. • Decreased – skeletal class III malocclusion • Mandibular plane angle- SN plane and mandibular plane • ( Go-Gn) • Average value- 32 0 • Increased –vertical growth pattern. • Decreased –horizontal growth pattern • Occlusal plane angle- between occlusal plane and SN plane • Average value- 14 0 STEINER’S DENTAL ANALYSIS • Upper incisor to NA ( angle)long axis of upper incisor and a line joining nasion to point A. • Average value- 22 0 • Increased –proclined upper incisors. • Decreased – retroclined upper incisors. • Upper incisor to NA ( linear)linear measurement between labial surface of upper incisor and line joining nasion to point A. • Average value- 4 mm • Increased –proclined upper incisors. • Decreased – retroclined upper incisors. • lower incisor to NB( angle)- long axis of lower incisor and a line joining nasion to point B. • Average value- 25 0 • Increased –proclined Lower incisors. • Decreased – retroclined lower incisors. • Lower incisor to NB ( linear)linear measurement between labial surface of lower incisor and line joining nasion to point B. • Average value- 4 mm • Increased –proclined lower incisors. • Decreased – retroclined lower incisors. • Interincisor angle- long axis of upper and lower central incisors. • Average value- 130-1310 • Increased –angle’s class II division 1malocclusion. • Decreased –angle’s class II division 2 malocclusion. SOFT TISSUE ANALYSIS • Lip in a well balanced face should touch a line extending from soft tissue contour of the chin to the middle of an “s” formed by the lower border of the nose. TWEED ANALYSIS • Three planes that makes a diagnostic triangle. I. Frankfort horizontal plane II. Mandibular plane III. Long axis of lower incisor • • • • Frankfort mandibular plane angleMean value-250 Incisor mandibular plane angle Mean value-900 • Frankfort mandibular incisor angle• Mean value-650 WITS APPRAISAL The purpose of Wits appraisal is to identify instances in which the ANB reading does not accurately reflect the extent of anteroposterior jaw dysplasia. Shortcomings of ANBThe anteroposterior spatial relationship of the jaws relative to the cranium.e.g. prognathus face- ANB increases. Retrusive jaws- ANB reduced. WITS APPRAISAL • Rotational effect of • jaws relative to cranial • base on ANB- • Clockwise rotation- ANB increases. • Anticlockwise rotation- ANB decreases. WITS APPRAISAL • When ANB angle is not reliable. • Functional occlusal lane • AO • BO • Distance between AO AND BO • In males pint BO ahead of AO by 1mm. • In females AO and BO coincides. DIGITAL CEPHALOMETRY • Software's for cephalometry. REFERENCES • Radiographic cephalometry: from basics to video imaging. Alexander Jacobson. • Contemporary orthodontics. 5th edition. William R Proffit • Orthodontics : the art and science. 4th edition. S I Bhalaji