Practical pathology
advertisement

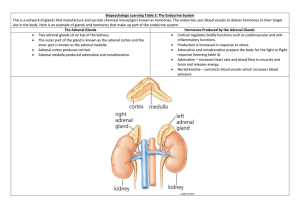
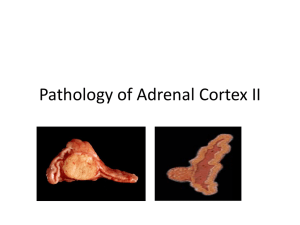
PTH Adenoma Normal Parathyroid Primary Hyperparathyroidism Parathyroid adenomas are • mostly composed of fairly uniform, polygonal chief cells with small, centrally placed nuclei Primary parathyroid hyperplasia • usually involves all 4 glands (up to 1 gm total). It is composed of chief cells and can be sporadic or associated to MEN In parathyroid hyperplasia, there is little or no adipose tissue, but any or all cell types normally found in parathyroid are present. Note the pink oxyphil cells here. This is actually "secondary hyperparathyroidism" with enlarged glands as a consequence of chronic renal failure with impaired phosphate excretion. The increased serum phosphate tends to drive serum calcium down, which in turn 7 drives the parathyroids to secrete more parathyroidhormone. Parathyroid hyperplasia is shown here. Three and one-half glands have been removed (only half the gland at the lower left is present). Parathyroid hyperplasia is the second most common form of primary hyperparathyroidism, with parathyroid carcinoma the least common form. 8 From AAFPweb h13 Zona Glomerulosa • Zona Fasiculata • Zona Reticularis • Massive adrenal haemorrhage, resulting in primary acute adrenal insufficiency Metastatic breast carcinoma affecting the adrenal gland and causing primary chronic adrenal insufficiency This is a caseating granuloma of tuberculosis in the adrenal gland. Tuberculosis used to be the most common cause of chronic adrenal insufficiency. Now, idiopathic (presumably autoimmune) Addison's disease is much more 15 often the cause for chronic adrenal insufficiency. Adrenal Cortical Adenoma Adrenal Adenoma Cortical Carcinoma Adrenal Carcinoma