Endocrine System Overview: Anatomy, Hormones, & Assessment
advertisement

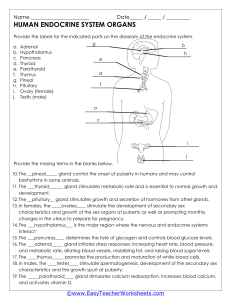
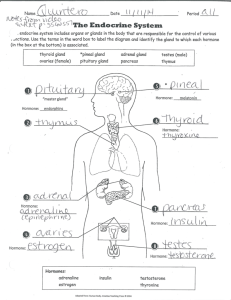
Chapter 18 Endocrine System Endocrine System Anatomy and Physiology Review • • • • • • • Hypothalamus Pituitary glands Gonads Adrenal glands Thyroid gland Parathyroid gland Pancreas Hormone-Receptor Binding Positive and Negative Feedback System Negative Feedback • Gland X releases hormone X this stimulates target cells to release hormone Y • When there is an excess of hormone Y gland X senses this and inhibits it release of hormone X Hypothalamus Endocrine Glands: Adrenal Glands • Adrenal cortex—mineralocorticoids (aldosterone), corticosteroids (cortisol) • Adrenal medulla—catecholamines (norepinephrine and epinephrine) Thyroid Gland • Control of metabolism • Calcium and phosphorus balance Parathyroid Gland • Parathyroid hormone (PTH) • Calcium • Phosphorous Pancreas Assessment Methods • Patient history • Nutrition history • Family history • Genetic risk • Current health problems Assessment Methods • Current health problems including any changes in: • • • • Energy levels Elimination Sexual and reproductive functions Physical appearance Physical Assessment • Examine for: • • • • • • • Prominent forehead or jaw Round or puffy face Dull or flat expression Exophthalmos Vitiligo Abdominal Striae Hirsutism Palpation Only gland that can be palpated Laboratory Tests • Stimulation/suppression tests • Assays • Allows for many different hormones to be analyzed at the same time • Urine tests • 24 hour • Tests for glucose • HbA1C • Imaging assessment • Other diagnostic assessment • Needle biopsy Review Chapter 18 Study Guide