Title: The Parathyroid Gland, Adrenal Gland, Pancreas and their
advertisement

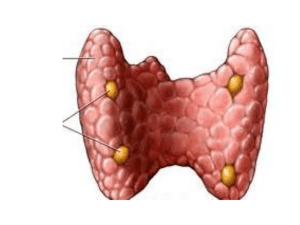
Title: The Parathyroid Gland, Adrenal Gland, Pancreas and their Secretions 1- The Parathyroid Gland – The parathyroid gland secretes parathyroid hormone, which regulates calcium, magnesium and phosphate levels a- The parathyroid glands are small (usually four) little glands embedded in the posterior surface of the thyroid gland b- Each gland weighs about 0.04 grams, and contains two types of cells 1- the more numerous Chief cells that produce the parathyroid hormone 2- and the less common oxyphil cells whose function is not known, however they do not regularly appear until after pituitary 2- Parathyroid Hormone a- The parathyroid hormone is the major regulator of calcium, magnesium and phosphate ions in the blood b- Blood calcium levels directly controls the secretion of calcitonin and parathyroid hormone through negative feedback loops. c- The two hormones have opposite effects on the blood calcium 1234567- PTH increases the number and activity of osteoclasts which releases calcium and phosphate in the bone into the blood. PTH also acts on the kidneys by slowing the rate at which calcium and magnesium are lost in the urine. It also increases the loss of phosphate in the urine. This decreases blood phosphate levels and therefore increases the levels of calcium and magnesium in the blood. PTH also stimulates the production of calcitriol which increases the rate of absorption of calcium and magnesium from the GI tract into the blood. 8- Diagram 3- The adrenal cortex secretes mineralcorticoids and androgens. The adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine a- The paired adrenal glands (suprarenal) glands lie on top of the kidney’s b- The adrenal gland is divided into two portions: the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla c- The adrenal gland, like the thyroid gland is highly vascularized d- The adrenal cortex produces steroid hormones that are essential to life. Complete loss of the adrenal gland leads to death due to dehydration and electrolyte imbalance in several days unless replacement therapy is started right a way. The adrenal medulla produces epinephrine and norepinephrine 4- The Cortex a- The cortex is divided into three zones, each of which secretes a distinctively different type of hormone 1- The outer zone produces hormones called mineralcorticoids that effect mineral homeostasis 2- The middle zone produces the glucocorticoids which effect glucose metabolism 3- The inner zone producers small amounts of androgens, which are steroid hormones that have masculinizing effects 4- Diagram b- Mineralcorticoids – 1- Aldosterone is the major mineralcorticoid it regulates the metabolism of sodium and potassium ions. 2- Aldosterone increases the reabsorption of sodium from the urine into the blood and stimulates the secretion of potassium into the urine 3- Aldosterone also adjusts blood pressure and blood volume 4- Secretion of aldosterone is controlled by the angiotensin-aldosterone pathway. This can be summarized as such. Dehydration, low blood sodium or hemorrhage all of which lead to low blood volume and decreased blood pressure activate this system a- Decreased blood pressure stimulates the kidneys to release Renin into the blood b- in turn this activates angiotensin I, which as it passes through the lungs is converted to angiotensin II c- Angiotensin II causes contraction of smooth muscle, resulting in vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure d- Angiotensin II Stimulates the adrenal cortex to release aldosterone. This causes sodium to move from the urine into the blood. And causes potassium to move from the blood into the urine e- This causes more water to return to the blood from the urine and raises blood volume. This in association with the constriction of the smooth muscle returns blood pressure back to normal c- Glucocorticoids – 1- The glucocorticoids regulate metabolism and resistance to stress. The glucocorticoids include cortisol, hydrocortisone, corticosterone and cortisone. 2- The glucocorticoids have the following effects a- Protein breakdown b- Glucose formation c- Breakdown of Triglycerides d- Resistance to stress e- Anti-inflammatory effects f- Depresses immune response