File
advertisement

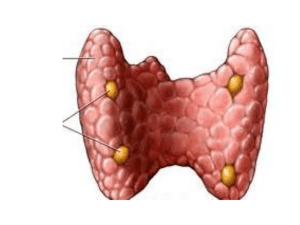
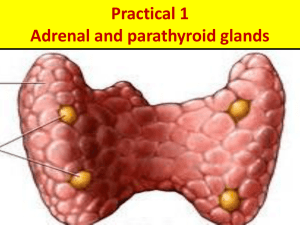
Disorders of the Thyroid Gland: • Goiter: results from an enlarged portion of the thyroid gland • May result from either hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism Parathyroid Gland Para means beside or alone or on top! • Four small glands embedded in the back of the thyroid gland • Secretes one hormone: PTH (parathyroid hormone) or (parathormone) when calcium levels in the blood are below normal Parathyroid Gland • Increases calcium by: • Increasing the # of bone-destroying cells, therefore releasing the calcium from storage in the bones • Increasing calcium re-absorption in the kidneys • Increasing the uptake in the digestive tract. • Works antagonistic to calcitonin Disorders - Parathyroid • Tetany: not enough parathyroid hormone, low blood calcium – neurons depolarize without a stimulus, resulting in twitches, spasms and convulsions • Osteitis fibrosa cystica: too much parathyroid hormone, high blood calcium – softening and demineralization of bones, calcium deposits in kidneys and other organs Do Section 13.2 Review page 450 # 1-7 The Adrenal Glands: • 2 Adrenal Glands: one above each kidney • Each of the glands contains: adrenal medulla and adrenal cortex Adrenal Medulla: • Actually part of the Sympathetic Nervous System (part of ANS) • Hormones are epinephrine (Adrenaline) • Part of the short term stress response Adrenal Medulla: • Epinephrine released as a response to stress– Glucose is released (glycogen is broken down) – Heart Rate increases – Breathing rate Increases – Iris dilates and pupil gets larger – Increased CNS alertness – Increased blood Pressure (to ensure blood is getting to the vital organs) – Other activities are inhibited (bladder, stomach) So what is an EpiPen used for? Alpha receptors are found on the walls of blood vessels. When adrenaline stimulates these receptors this causes the blood vessels to narrow, which stops the blood pressure from falling too low. It also redirects blood to vital organs like the heart and brain. Beta receptors are found in the heart and lungs. When adrenaline stimulates these receptors this relaxes and opens the airways, making breathing easier. It also stimulates the heart, making it beat faster and stronger Adrenal Cortex: • Part of the long term stress response • Secretes three types of steroid hormones: • Aldosterone (mineralocorticoids) • Cortisol (Glucocorticoids) • Sex Hormones (in small amounts) (Gonadocorticoids) Aldosterone: • Causes blood to absorb Na+ from distal tubule and expel/secrete K+ • Causes reabsorption of water into blood by working on the distal tubule (Remember that water follows solute!!) • Secretion is not only stimulated by the anterior pituitary’s release of ACTH but also by a rise in the K+ in the blood Cortisol: • Helps to resist and recover from stress Affects glucose levels by: • Stimulates protein degradation so amino acids are available for glucose production • the liver converts Amino Acids into carbohydrates when stores are depleted • Breaks down lipids into free fatty acids, which other tissues can use for metabolism so that glucose can be saved for the brain • Inhibiting glucose uptake and use by certain tissues so it can be spared for the brain Cortisol: • Polarised light micrograph of cortisol, or hydro- cortisone, the chief steroid hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex. Cortisol plays a role in both normal carbohydrate metabolism and in the body's response to physical & emotional stress. Sex Hormones: • Small secondary sex characteristics