Glacial Landforms 2
advertisement

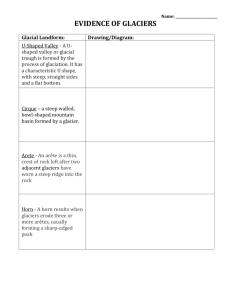
GLACIAL LANDFORMS SHAPE MOUNTAINS • • • • Surface features subglacial erosional depositional 1) Glacier travel: Surface features Crevasses: – V-shaped structures found in the uppermost layer of the glacier. WHY? – brittle deformation – Rarely > 20 m deep Accumulation area is often heavily crevassed Direction of flow New Zealand Bergschrund: crevasse that separates flowing ice from stagnant ice at the head of a glacier Glacier on Shorong Yul-lha, Nepal Icefall: steep, cracked and jumbled ice flows over a drop-off - fast moving!!!! Khumbu Ice fall, Everest Ogives: alternate bands of light and dark ice on a glacier Séracs: •Ice towers •Formed by intersecting crevasses, •rapid flow •steep slopes Glacier des Bossons, French Alps photo: MH Penitentes: spiky columns of snow; formed in dry environments Nev. Coropuna, Peruvian Andes Melt stream: Glacier can have streams on their surface!! Moulins Very slushy and slippery!! water SUB-GLACIAL STREAMS ICE CAVE AT BOTTOM OF GLACIER Pastoruri, Peru EROSIONAL LANDFORMS OVERVIEW CIRQUE •a semicircular or amphitheater -shaped bedrock feature created as glaciers scour back into the mountain. •This is where the snow and ice forming the glacier first accumulates. HANGING GLACIER Occur in tributary glaciers, cause spectacular waterfalls ARÊTE •steep-sided, sharp-edged bedrock ridge formed by two glaciers eroding away on opposite sides of the ridge HORN •a pyramid-shaped mountain peak created by glaciers eroding away at different sides of the same mountain. COL •a low spot or pass along a cirque or an arete. GLACIAL POLISH Result of abrasion by sand at bottom of glacier STRIATIONS •result of individual particles embedded in the glacier scratching the underlying bedrock. •lines indicate the orientation of glacial flow. NUNATAK •Peak surrounded by glaciers but not itself glaciated TARN •a glacial lake produced by scouring •often found in cirques. U-shaped valleys • a glacially eroded valley • large, flat valley bottom ROCHE MOUTONNÉE sheepback , or sheep rock large rock knob that resembles a grazing sheep DEPOSITION LANDFORMS Moraines •an accumulation of unconsolidated material deposited by glaciers •unsorted material (different sizes of particles) particles deposited in moraines •material has angular edges. TERMINAL OR END MORAINE •deposited at the snout end of a glacier •marks the furthest advance of a glacier •caused as a glacier retreats End morraine LATERAL MORAINE unconsolidated material deposited along the sides of an alpine glacier. Lateral morraine MEDIAL MORAINE When two alpine glaciers flow together, their lateral moraines join, forming a medial moraine MORAINES: OVERVIEW Medial Moraine ERRATICS Large boulders left by glaciers in areas where they obviously don’t belong. Can be 10’s to 100’s of kilometers form point of origin GLACIER LANDFORMS OVERVIEW