Vocabulary 7C
advertisement

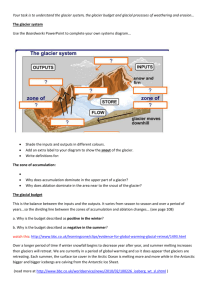
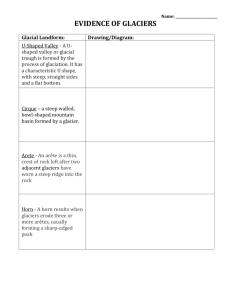
Vocabulary 7-C Glacier: a large mass of naturally formed ice on land that gradually moves downhill due to gravity Drumlin: a long, narrow, streamlined oval mound of unsorted sediment that is formed at the bottom of glaciers (usually continental ones) Glacial groove: a long narrow channel or furrow on bedrock formed by the gouging or sanding actions of rocks and sediments frozen to the bottom of a glacier; show the direction of former glacial movement Moraine: a mound, ridge, or sheet of unsorted, unlayered sediment deposited directly from an edge or the bottom of a glacier; types: lateral, medial, terminal, and end U-shaped valley: the characteristic shape of a valley after it has been eroded by glaciers, especially mountain glaciers; as compared to V-shaped valleys Finger lake: a body of water that forms in a long, narrow, U-shaped valley often partly dammed at one end by a mound of glacial moraine sediment; example: The Finger Lakes of central New York Glacial erratic: a boulder transported and deposited by a glacier having a lithology different than the bedrock upon which it is sitting. Kettle lake: a lake formed when a large block of ice buried in glacial sediment melts, leaving an oval depression which becomes filled with water; very common in New York State Esker: ridge formed from drift deposited in tunnels running through a glacier. Eskers are often mined for gravel and sand. Sediment: particles or materials formed by the weathering and erosion of rocks or organic materials; materials transported by erosional systems