Diabetes Mellitus: Case Study, Symptoms & Treatment

Diabetes mellitus
Defintion
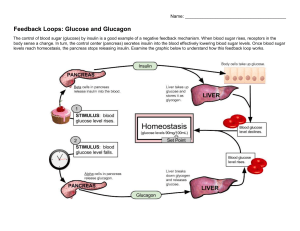
: Syndrome of disorderd metabolism result in high blood sugar( hyperglycemia).
Types:
1 Type 1:
Due to loss of insulin producing cells ( beta cells ) in the pancreas leading to insulin deficiency.
2Type 2 :
Due to reduced insulin secretion or insulin resistance.
Signs and Symptoms:
1 – The triad of polyurea, polydepsia and polyphagia.
2 – Visual changes and blurred vision.
3 – Smell of acetone in patient breath.
4 – Nausea, Vomiting and abdominal pain.
5 – Unexplained weight loss.
Investigations:
1 – Urine analysis: Kidney excrete sugar in urine when blood sugar is
150 mg/ dl.
2 – Blood analysis: aNormal fating venous blood sugar: 120 mg/dl. bRandom venous blood sugar: 200 mg/dl. cPost prandial blood sugar: 200 mg/dl.
1
Measures higher than that measures indicate Diabetes mellitus.
Diagnosis:
Depends mainly on the investigations
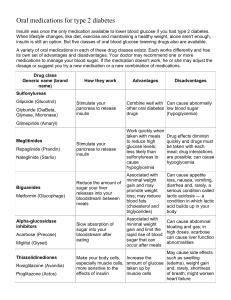
Treatment:
Depends on the measures.
By Trial and error.
3 - agents that increase the sensitivity of target organs to insulin as Metformin.
4 - agents that decrease the rate at which glucose is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract as Acarbose.
5 - Special diet regime.
6
– Exercise.
7 - Weight loss.
8 – Self home glucose monitor: with educated patients.
9
– Combination of drugs are used and to reach to ideal blood glucose level depends on the cooperation of the patient ,experience of the doctor and mainly on trial and error.
1Insulin and used in type 1 and complicated type 2. It is of many types.
2 - agents that increase the amount of insulin secreted by the pancreas as Sulfonylurease.
2
Case no.1:
A patient complain from weight loss.
When discussed by the doctor find that he complain also from polyurea, polydepsia and polyphagia.
The doctor discovered that he have blurring of vision and smell aceton in his breath.
1What you suspect?
2What investigations you do?
3What is the treatment?
3