All About Macromolecules
advertisement

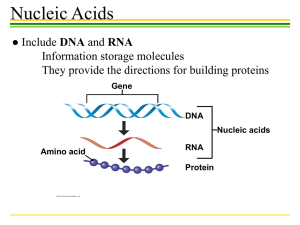
Macromolecule Notes Macromolecules: Proteins, Lipids, Polysaccharides (Carbohydrates) and Nucleic Acids Monomer: single building block for a macromolecule Proteins (polypeptides) Monomer: amino acid (a.a.) Compound in your body with nitrogen, carbon, oxygen and hydrogen 20 essential amino acids in your body Linked by a peptide bond Examples: o Beef o Hair o Eggs o Hemoglobin (blood component) o Insulin (lacking in diabetics to process sugar) o In muscles Lipids (fats) Monomer: glycerol and 3 fatty acids QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Saturated Fats o All single bonds in the fatty acids o Bad for you: the bonds allow the fats to clump and clog arteries Unsaturated Fats o Double bonds in the fatty acids Examples: o Butter o Oil o Cholesterol Polysaccharides (carbohydrates) Monomer: monosaccharides (sugars) QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. o Usually glucose (six-sided sugar) Examples o Bread o Cereal o Potatoes o Fruits (fructose) o Pasta Nucleic Acids (DNA/RNA) Monomer: nucleotide (sugar, phosphate, base) QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Adenine-A Guanine-G Cytosine-C Thymine-T Sugar: Deoxyribose Double Helix Stays in nucleus DNA Vs. RNA Adenine-A Guanine-G Cytosine-C URACIL-U Sugar: Ribose Single Strand Genetic messenger-moves around cell RELATING TO THE CELL: Energy Structure/Support Cell-Cell Communication Carbohydrates: 1. Monosaccharides Made during photosynthesis Energy source Examples Glucose Fructose (fruit sugar) Galactose (milk sugar) 2. Disaccharides Combinations of monosaccharides Energy source Examples Glucose + glucose = maltose Glucose + galactose = lactose Glucose + fructose = sucrose 3. Polysaccharides Combinations of mono- and disaccharides Energy Storage Starch in plants Glycogen in animals Structural Support Cellulose in plants: Cell wall Chitin in animals: Exoskeleton Cell-cell communication/recognition/adhesion Glycolipids Glycoproteins Found in cell membrane FATS and the Cell: All fats is hydrophobic (water-hating) 3 types: o Triglycerols o Phospholipids o Steroids Triglycerols: 1 glycerol & 3 fatty acids Energy storage Cushions/Insulates body/nerves Examples: Fats/Oils Phospholipids: 1 glycerol, 2 fatty acids, phosphate group (hydrophilic) Make up phospholipids bilayer of cell membrane Steroids: VERY hydrophobic Help maintain membrane fluidity (Cholesterol) Sex hormones: testosterone, estrogen, progesterone