CARBOHYDRATES (Polysaccharides) NUCLEIC ACIDS
advertisement

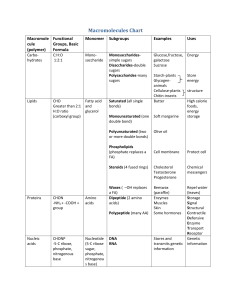
CARBOHYDRATES (Polysaccharides ) Building block: MONOSACCHARIDES NUCLEIC ACIDS (Polynucleotides) Building block: NUCLEOTIDE = Phosphate + Sugar + Nitrogen Base LIPIDS (FATS) (Triacylglycerols) Building block: GLYCEROL +FATTY ACIDS Fatty Acids - saturated unsaturated Ex. glucose FUNCTIONS: Energy Storage glycogen (animals) starch (plants) Structural cellulose FUNCTIONS: Energy Storage - Fats Protection - Waxes Messengers - Steroids Structural - Membranes FUNCTIONS: Information Storage - DNA & RNA Energy Transfer - ATP In Membranes: Phospholipids One fatty acid is replaced with a phosphate group • All of the above use glucose as the building block - only the arrangement is different Cell/Cell Recognition and Communication (oligomers) Amphipathic: have hydrophobic & hydrophillic regions PROTEINS (Polypeptides) Levels of Protein Structure: Primary (10 ) = Covalently bonded polymers of amino acids Secondary (20 ) = á helix or â sheet configurations • H-bonds between carboxyl-O of one aa and the amino-H of a non-adjacent aa. Tertiary (30 ) = sum total or all á helix and/or â sheet configurations • Hydrophobic interactions, H-bonds, ionic bonds, and covalent bonds (disulfide bridges) between R-groups Quaternary (40 ) = Protein subunits combine to form single multisubunit protein Building block: AMINO ACID ! 20 different amino acids FUNCTIONS: Structures: eg. Collagen Enzymes