1406 final exam guide.doc
advertisement

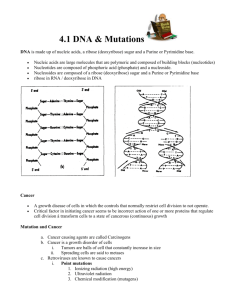
Houston Community College (Town & Country) Final Exam Study Guide Dr. H. I. Chukwu • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • What is genetic recombination. What is the wild type Cchromosome map. The chromosomal basis of sex varies with the organism (human, grasshopper, chicken and bees) ex. XY, XO, ZW Sex linked genes are more likely to be inherited by males or females What is Duchenne muscular dystrophy What is a linked gene What is Nondisjunction, at what stage of meiosis does this occurs? Types of changes in chromosome structure.( deletion, duplication invertion, reciprocal translocation What is the relationship between aneuploid and Down syndrome What are phages. Transcription can be separated into three stages. What are the stages (initiation, elongation, and termination) What are mutations, point mutations What are pathogens,, cuspid, host range, phage Viruses can reproduce by two alternative mechanisms? What is a retrovirus, Viroids The first vaccine developed to fight smallpox Classification of viruses Characteristics of virus What is an obligate parasite? What makes up the viral envelopes What caused the horizontal transmission of plant viral diseases What is R plasmid What are conjugation, mutation, transduction Why are linked genes inherited together? Crossing over occur at what phase What affects the frequency of crossing over between linked genes What are the chromosomal system for determining sex in animals Independent assortment is? Syndrome, who are affected What are deletion, disjunction, inversion, translocation, duplication? What is a tetraploid? DNA is made up of? What type of bond holds DNA together? Functions of DNA polymerase Differences between DNA and RNA Genetic recombination What is The human genome project What are examples of purines: pyrimidines Effects chromosomal mutations