ELECTROMAGNETIC INTERFERENCE (EMI) Eric Mitchell Phil Zanotti
advertisement

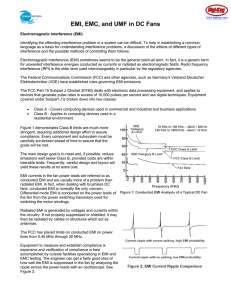
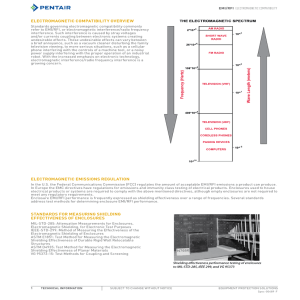
ELECTROMAGNETIC INTERFERENCE (EMI) Eric Mitchell Phil Zanotti Kasra Dabiran Leon Voskov Ross Schwarz OVERVIEW Introduction Examples Wireless Devices Natural Interferences Switching Circuits Radio Frequency Electromagnetic warfare Prevention and Mitigations Techniques Standards and Regulations Summary BACKGROUND What is EMI? Electromagnetic Interference is disturbance that affects an electrical circuit Caused by induction or outside radiation Can temporary and permanently disrupt circuit components Big design issue for new products HOW DOES EMI WORK? Causes Electric fields radiating from currents Switching circuits, clocks, natural fields, ect. Coupling of electric fields into circuits and components Unintentional and intentional Effects Causes problems for electronics Loss and disruption of data Growing problem with more advanced devices EXAMPLES OF EMI SOLAR INTERFERENCE 2012 Solar Maximum 11 year solar cycles Flight routes over north pole changed Solar Storm of 1859 March 1989 Solar Storm X-class solar flare Power outage in Quebec Communications with some satellites disrupted for hours Other potential issues Spacecraft communication Induced currents on underground piping HF radio interference INTERFERENCE AT 2.4 GHZ Why use 2.4GHz? Devices and protocols Part of the ISM Band that operate in this band No license needed to design Cordless telephones devices in this range FCC originally designated 2.4-2.483 GHz band for microwave ovens Baby monitors Bluetooth Wi-Fi 802.11b and 802.11g wireless devices (most routers) Wireless cameras and controllers CELLULAR DEVICE INTERFERENCE Airplanes No proven scientific basis for banning cell phone use on airplanes FAA, FCC, and aircraft OEMs are unwilling to spend money to do testing Ban on cell phone use errs on the side of caution Medical Equipment 2007 Mayo Clinic study showed that phones have no negative effect on medical equipment FDA has developed standards for pacemaker OEMs to ensure safety POWER CONVERTERS Capacitive, Inductive, and Resistive loads Caused by sudden load changes Found in many household items Computers, phone chargers, TVs, etc. Minimal or no EMI effect created ELECTROMAGNETIC PULSE Intense surge of electromagnetic radiation Created using high-energy explosion (i.e. nuclear) Gamma rays trap high-energy electrons in earth’s magnetic field Destroys all power electronics connected to affected power grid RADIO FREQUENCY INTERFERENCE Two way transmitters, radio stations, amateur radio broadcast Interrupted signal before reaching receiver Results in signal masking and distortion PREVENTION AND MITIGATION EMI FILTERS AND CHOKES Coil of wire wound around magnetic core Blocks high-frequency AC in a circuit Passive inductor Impedance is proportional to frequency Simple and inexpensive Energy Reflected back up the cable Absorbed resistively within ferrite core (heat) Audio vs. Radio ELECTROMAGNETIC SHIELDING Shields Enclosure formed by conducting material Isolates electrical devices and blocks external electric fields Often known as Faraday Cage (invented in 1836) Amount of reduction depends Material and its thickness Size of shielded volume Frequency of fields Examples Cables MRI scan room Microwave oven Electronic devices MITIGATION SOFTWARE AND TECHNIQUES EMI Analyst is a tool used for meeting EMI requirements set by regulatory agencies Combines all four areas of EMI analysis Conducted Emissions Radiated Emissions Conducted Susceptibility Radiated Susceptibility Money Saving Tool Reduction of circuit design area FINAL EMISSIONS SCREENSHOT STANDARDS AND REGULATIONS EMI TESTING PROCEDURE REGULATION COMMITTEES FCC Federal Communications Commission United States Modems, Printers, and other I/O devices CISPR The International Special Committee on Radio Frequency Interference International House hold appliances, Ignition systems, fluorescent lamps CLASSES OF REGULATIONS Class A Class B “A computing device that is marketed for use in a commercial, industrial, or business environment; exclusive of a device which is marketed for use by the general public, or which is intended to be used in the home.” “A computing device that is marketed for use in a residential environment notwithstanding use in a commercial, business, and environmental environments.” FCC AND CISPR CLASS A FCC AND CISPR CLASS B OTHER TYPES OF STANDARDS MIL-STD-416D CE - Conformité Européenne Department of Defense European Conformity Even harder-to-meet standards Identifies that a product or than FCC and CISPR Dependent on reliability of electronic and communication equipment machine is compliant with all safety requirements Requirement not a voluntary process CONCLUSION Introduction and Background Examples of Electromagnetic Interference Prevention and Mitigation Techniques Laws and Regulations Questions?