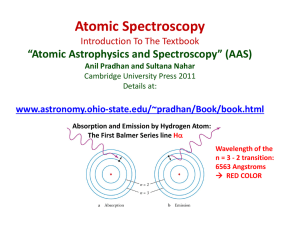
Electromagnetic Interference

Electromagnetic
Interference
Hospital Device Immunity
RF Transmitters
RF Transmitters – 2 Major Categories:
1.
Intentional
Portable (handheld or mobile):
Cellular Telephones, 2-Way Radio, Telemetry
Installations:
Paging Tower, Broadcast, Radar
2.
Unintentional
Electrically powered equipment including Medical
Devices
Nature
RF Transmitters
Effective Radiated Power
Function of Output Power and Antenna
Efficiency
Usually fixed except Cellular
More power = greater range at same wavelength
RF Transmitters
Field Strength (V/m)
Distance dependant
In free space far field strength is inversely proportional to distance
Reflections can cause higher than expected strength
Referenced to wavelength
RF Transmitters
Wavelength
Short wavelength (high frequency) more problematic than long wavelength (low frequency)
Conductors measuring ¼ or ¾ of the wavelength are most susceptible to interference
RF Propagation
1.
2.
3.
Radiation
Transmitter and Receiver
E.g. Radio or TV Broadcast Transmission
Conduction
Physical connection
Does not need to be directly coupled
E.g. ESU coupled to Pt. monitor via Pt.
Induction
Magnetic or Capacitive coupling
E.g. signal cables routed parallel to each other
EMI Induced Problems
1.
Bit Corruption
Associated with digital devices
Artifact changes byte value
Usually fixed with error detection schemes
2.
Junction Rectification
Associated with analog devices
High frequency AC produces DC at semiconductor junction
Produces DC off set voltage or modulated signal
Electric Field Strength in Hospital locations
(500 kHz to 1.5 MHz)
Nursing Unit 0.5 – 2.0 V/m
Radiology Room
Emergency Room
Operating Room
0.5 – 3.0 V/m
5.0 – 10.0 V/m
30.0 V/m
(1m from active ESU)
Ad Hoc Testing
Simultaneous learning, test design and test execution.
Informal, one time testing with no designed procedures.
Flexible, customized procedures for task at hand.
Generally exploratory in nature – sometimes called Exploratory
Testing.
Ad Hoc Testing
Must incorporate reporting procedure
Need a method to quantify and compare data collected
Test data should be reproducible!
Useful for defining formal test procedures.
Electromagnetic
Vulnerability
Medical Device Selection
Criteria
Electromagnetic Vulnerability
1.
Criticality of the Device
Is it life supporting
Critical patient monitoring
Diagnostic
Medication delivery
2.
Impact of Device Failure
Potential of injury or death to patient
Can it cause harm to staff
Electromagnetic Vulnerability
3.
Compliance with applicable EMC
Standards
Has the device been tested for EMC by an outside party?
4.
Known EMI Problems with Device
Type of device, model or manufacturer history.
5.
Suspected EMI Problems with Device
Erratic performance of device
Electromagnetic Vulnerability
6.
Sensitive Components or Circuitry
High gain amplifiers, microprocessors, patient leads, any antenna resembling traces
7.
Frequent No Fault Found Repairs
Repeated reported issues with device yet testing reveals no anomalies OR problems disappear when removed from user area
Device Immunity to RF
Hospital devices have conductors of various lengths.
Many of these devices are designed to amplify very weak signals.
Many of these devices have connecting wires that can act as antennas.
EMI Recognition
Device works in shop but is erratic on floors.
Patient’s condition does not match data provided by device.
Intermittent malfunction during certain weather conditions or when transmitter is nearby.
Inexplicable alarms