Nervous System 2

Brain and Cranial Nerves
Bio 40B
Dr. Kandula
Brain
Part of CNS
Found in dorsal body cavity
Continuous with spinal cord at foramen magnum
The development and uniqueness of brain makes humans “ superior ” to other animals
Brain
Enclosed and protected by the cranium and three membranes called meninges
Dura Mater
Arachnoid Mater
Pia Mater
Meninges of Brain
Meninges
-
-
Three membranes that surround and protect the brain
Dura mater outermost tough fibrous membrane
Made up of 2 layers : outer periosteal layer is attached to cranium; inner layer surrounds brain
Meninges of the Brain
• There are 3 inward folds of dura mater:
• Falx cerebri: Goes into longitudinal fissure separating two cerebral hemispheres
• Falx cerebelli: Separates the 2 hemispheres of cerebellum
• Tentorium cerebelli: Separates cerebrum from cerebellum
Meninges
Arachnoid lies deep to dura mater and is separated from it by subdural space , this space contains small amounts of interstitial fluid. The arachnoid is an avascular layer.
Pia mater lies deep to the arachnoid layer and is separated from it by the subarachnoid space.
The subarachnoid space contains cerebrospinal fluid . The pia mater is tightly attached to surface of brain.
Brain
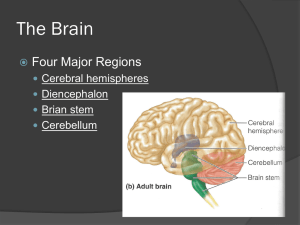
Made up of 4 parts:
The four parts include: cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, brainstem and cerebellum.
Sectional view of Brain
Brain
In humans the cerebrum is the most prominent part and makes up 70 % of the brain
Cerebrum
Separated into two hemispheres by longitudinal fissure
Falx cerebri found in fissure
Corpus callosum (white matter fibers) connects two hemispheres at base of fissure
Cerebrum
Gyri (pl) or gyrus (sing) are ridges
Sulci (pl) or sulcus (sing) are shallow grooves
– central sulcus,
– parieto-occipital sulcus,
– lateral sulcus
Fissures are deeper grooves
– longitudinal fissure
– transverse fissure
Superior view of Brain
Cerebrum
Cortex: Thin outer edge of gray matter (neuron cell bodies)
Thick central core of white matter (axons)
Four lobes
– Parietal: receives sensory info
– Frontal: voluntary motor
– Occipital: vision
– temporal: hearing, taste
Cerebrum
Important gyri
Precentral gyrus – primary motor area, ie. all impulses for voluntary muscular activities originate here.
Postcentral gyrus – primary sensory area, ie., all general senses information perceived here
Functional areas to know:
Primary motor, primary somatosensory, somatosensory association, vision, hearing
Diencephalon and Brain stem
Diencephalon
1. Thalamus
Mostly gray matter
Relays sensory info to cerebrum
2. Hypothalamus
“ master gland ” of body
Controls hormones, temp, emotion, thirst
Maintains homeostasis
Controls ANS functions
3. Epithalamus has pineal gland to control day/night cycles.
Brain Stem
1.
Medulla oblongata
White matter of motor and sensory neurons
This is where neurons cross to opposite side of body pyramids
Breathing and heart control
2.
Pons means “ bridge ”
Bridge between medulla and midbrain
Also contains breathing center/helps regulate breathing
3.
Midbrain
Corpora quadrigemina ,( superior and inferior colliculi) controls reflexes associated with hearing and vision
cerebral aqueduct (with CSF)
Cerebellum
Cerebellum
Also has 2 hemispheres connected by a body called vermis
Function: coordination, balance and equilibrium
Folds of gray matter folia
White matter arrangement characteristic and called arbor vitae
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Function: cushion/protect brain and spinal cord
Made by the ependymal cells of choroid plexuses (small capillaries in the ventricles)
Circulates through subarachoid space and the four ventricles
Finally, CSF drains out the arachnoid villi back into the blood circulation
Circulation of CSF
4 Ventricles of brain with cerebrospinal fluid
Circulation of CSF
Lateral ventricles foramen of Munro third ventricle cerebral aqueduct fourth ventricle central canal of spinal cord or subarachnoid space surrounding brain and spinal cord
Cranial nerves
Cranial nerves
Part of the peripheral nervous system
12 pairs that mostly control head and neck
Nerves contain motor neurons, sensory neurons, or mixed
See handout
III
IV
V
I
Number Name
II
VI
Olfactory
Optic
Innervation Type Function
Temporal lobe of brain sensory Smell
Occipital lobe of brain sensory Vision
Occulomotor Eye muscles and ciliary body mixed
Trochlear
Trigeminal
Abducens
Superior oblique muscle of eye mixed touch –pain– temperature to the face; motor division of the nerve supplies the muscles of mastication supply a muscle called the lateral rectus muscle that moves the eye outward. mixed mixed
Movement of eyeball
Movement of eyeball
Touch on face; mastication
Movement of eyeball
Numb er
VII
VIII
Name
Facial
Auditory
Innervation Type
Action motor portion supplies all the facial musculature/ sensory portion, taste to the anterior two-thirds of the tongue; secretory to the lacrimal gland and salivary glands
Temporal lobe of brain mixed facial musculature, taste, and tears & saliva secretion sensory Hearing and equilibrium
IX
X
Glossopharyngeal Pharynx, tongue and salivary glands mixed TASTE POSTERIOR
1/3 TONGUE,
SALIVATION,
SWALLOWING
Vagus Pharynx heart, respiratory tract,
GIT, mixed GASTRIC PANCREATIC
SECRETIONS, GI
MOVEMENT, CARDIAC,
RESPIRATORY AND
VISCERAL REFLEX
Number Name Innervation Type Action
XI
XII
Spinal
Accessory
Muscles of neck and shoulder mixed MUSCLE
MOVEMENT
(sternocleidomastoid, trapezius) AND
VISCERAL REFLEX
Hypoglossal Tongue muscles mixed Tongue movement