SHEEP BRAIN DISSECTION DIRECTIONS
advertisement

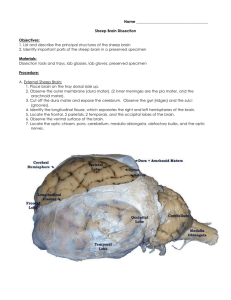
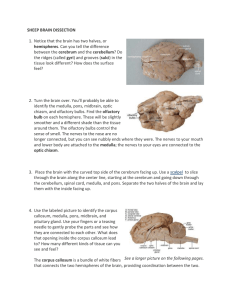
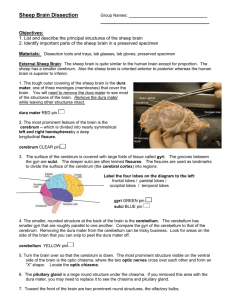
SHEEP BRAIN DISSECTION DIRECTIONS REMOVE DURA MATER FIRST: Carefully peel the dura mater off, using your blunt end scissors to cut it where it fits tightly between the cerebellum and the cerebrum. Some of the cranial nerves on the ventral side will come off as you pull on it. If you need help, ASK! 1. LOOK AT DORSAL VIEW IDENTIFICATION Diagram #1 Answer questions 1-4 as you complete this section. Locate and point out to your partner the following structures on the brain: Cerebrum, cerebellum, medial longitudinal fissure, spinal cord, medulla and sulcus. Most of the brainstem is not visible from the dorsal view. Make sure each person in your group can identify each part. Using the forceps OR blunt end probe, carefully and gently, spread apart the two hemispheres of the cerebrum until you see the heavy band of white fibers connecting the hemispheres called the corpus callosum. The thin saran wrap like covering is the pia mater the layer of meniges that protect the brain. DO NOT SEPARATE THE HEMISPHERES! Locate the cerebellum on which is posterior to the cerebrum on the sheep. In humans, the cerebellum is located inferior to the cerebrum. The brain has some dark and light structures. The lighter color is the white matter and the darker the gray matter. 2. LOOK AT LATERAL VIEW IDENTIFICATION Diagram #2 Answer questions 5-6 as you complete this section. Locate the following AND verbally tell your partner about these structures: spinal cord, cerebellum, cerebrum, optic nerve (if present), olfactory bulb (if present), and rhinal fissure. The rhinal fissure is present in all mammals, including man. 3. LOOK AT VENTRAL VIEW Diagram #3 Answer Questions 7-10 as you do this section. Locate the following: hypothalamus, pyriform lobe, midbrain, pons, medulla, spinal cord, cerebral peduncle, optic nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve(if present). 4. LOOK AT MEDIAL VIEW (Saggital cut) Diagram #4 Answer Questions 11-12 as you complete this section. Place the brain on the dissection tray ventral surface downward. Place the scalpel in the medial longitudinal fissure. With a smooth stroke, cut the brain saggitally--cutting through the cerebrum, the cerebellum and brain stem. Identify the following: thalamus, hypothalamus, pons, medulla, cerebrum, cerebellum, corpus collasum, III ventricle, IV ventricle. 5. PARTS OF THE BRAIN IDENTIFICATION CUTS DIAGRAM #4. Answer question 13. Using only one half of the brain, carefully dissect the following parts out and as you do, verbally tell your partner their names: The cerebellum, the thalamus, hypothalamus, medulla, pons, midbrain, corpus callosum, and cerebrum. 6. LOOK AT CROSS SECTION CUT Diagram #5, #6, #7 Using the other half of the brain, look at the diagram GUIDE TO CUTTING (#5), make both cross section cuts as shown. Do the cuts on only one half of the brain. IN cut “A”, note the depths of the sulci, and the contrast between the white and gray matter. Identify the corpus callosum, and the fissures shown in diagram 6. IN cross section “B” locate and verbally name these parts to your partner: the thalamus, hippo campus, corpus callosum, lateral ventricles, corona radiata, sulci and fissures as shown in diagram #7. FINISH QUESTIONS ON THE QUESTION SHEET. USE CLASS NOTES or TEXT FOR ANSWERS NOT IN THE LAB. NAME PER SCORE . SHEEP BRAIN DISSECTION LAB SHEET 1. What is the name of the fissure in the sheep brain that is between the hemisphere? 2. Why are some areas of the brain darker than the others? 3. What white structure connects the hemispheres? What type of tissue is it made up of? 4. What is another name for pia mater and acrahnoid mater? (use your notes for these answers) What is their function? 5. What is the difference in the location of the cerebellum and cerebrum in the human brain than in the sheep’s brain? What about size? 6. What parts of the brain stem are visible in the LATERAL VIEW (Diagram #2)? 7. What is the function of the olfactory bulb? (Look in notes or book) 8. What parts of the brain stem are visible in this view? 9. What is the other name for the hypothalamus and thalamus? (Look in class notes) 10. What does the optic nerve allow a sheep or human to do? What lobe of the human brain is it associated with? 11. What is the purpose of the ventricles? 12. What is another name for the cerebellum? 13. What are the functions of the medulla? 14. Which is the largest part of the sections you cut out? the smallest? 15. What do the two different colors in the cross sections viewed show? 16. What are two differences between the human brain and the sheep’s brain?