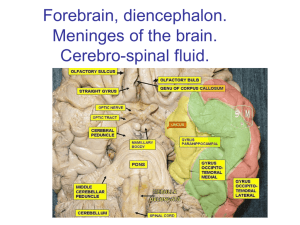
Brain Structure and Function
advertisement

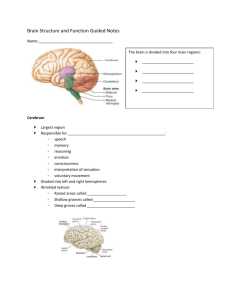
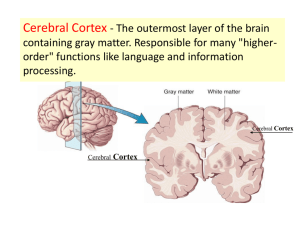
January 7, 2014 Click me! The brain is divided into four main regions: Cerebrum Diancephalon (aka interbrain) Brain stem Cerebellum Largest region Responsible for all ‘higher’ brain functions: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ speech memory reasoning emotion consciousness interpretation of sensation voluntary movement Divided into left and right hemispheres Wrinkled texture ◦ Raised areas called gyri ◦ Shallow grooves called sulci ◦ Deep groves called fissures The outer part of the cerebrum – called the cerebral cortex -is composed of gray matter ◦ Gray matter = cell bodies and unmyelinated nerve fibers ◦ This is where thought, sensation, etc. occur The inner part of the cerebrum is mostly white matter ◦ White matter = mylinated nerve fibers ◦ This is the connection between different regions of the brain The corpus callosum is one especially important area of white matter – it’s the connection between the two cerebral hemispheres Damage to one of these regions can cause loss of specific functions (e.g. partial paralysis due to stroke) BUT The brain does have some ability to heal itself – to form new connections or to have one hemisphere take over the job of the other hemisphere - this is called brain plasticity Jody’s story But also see Phineas Gage’s story The diencephalon consists of three parts: thalamus epithalamus (completely enclosed by thalamus) hypothalamus structures that are part of the diencephalon Regulation of autonomic functions, including ◦ Body temperature ◦ Water balance ◦ Metabolism Control of endocrine system Limbic system – emotional / visceral brain (sex, food, thirst, pain, pleasure) Mostly, these functions are done by the hypothalamus The brain stem consists of three parts Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Controls many autonomic functions, including: Breathing Blood pressure Heart rate Also allows passage of nerves fibers between brain and spinal cord Back of the brain, beneath cerebrum Like cerebrum, it has ◦ Two hemispheres ◦ Wrinkled surface ◦ Outer cortex made of gray matter outside and inner region of white matter Functions: • Balance • Coordination of muscles Do the diagrams and questions on your guided notes Following a stroke, a person develops the symptoms listed below. Which part of the brain was damaged? ataxia (an inability to coordinate muscular movement) cerebellum Drooping left side of face right cerebral hemisphere Fluid that surrounds and protects brain and spinal cord Produced by the choroid plexuses from blood plasma, and drains back into the blood Some diseases can be diagnosed by examining CSF collected during a spinal tap Which glial cells are involved with CSF? What do they do? Fluid that surrounds and protects brain and spinal cord Produced by the choroid plexuses from blood plasma, and drains back into the blood Some diseases can be diagnosed by examining CSF collected during a spinal tap Which glial cells are involved with CSF? ependymal What do they do? Circulate CSF Protects the brain from toxins, most drugs, and fluctuations in other chemicals such as ions Two major barriers ◦ Relatively impermeable brain capillaries ◦ Astrocytes which control flow of materials from blood vessels to neurons Why is the blood brain barrier necessary? Does the blood brain barrier block the passage of alcohol? Why is the blood brain barrier necessary? Without a controlled environment, uncontrolled neural activity might occur Does the blood brain barrier block the passage of alcohol? No – you can tell by the effects What were our objectives, and what did you learn about them. What was our learner profile trait and how did we exemplify it? How does what we did today address our unit question? For the following questions, A = cerebrum, B= diencephalon C = brain stem, D = cerebellum 1) The thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus constitute the _________________. 2) Control of temperature, endocrine activity, and thirst are associated with the ____________. 3) The area of the brain that controls breathing and heart rate is the _________________. 4) A shallow groove on the surface of the cortex is called a A) fissure C) furrow 5) B) gyrus D) sulcus The three major parts of the brain stem are the A) cerebrum, cerebellum, and diencephalon B) thalamus, epithalamus, and hypothalamus C) midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata D) basal nuclei, pineal body, and choroid plexus 6 7 8 9 EC 1 EC 2 10