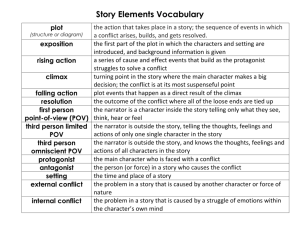
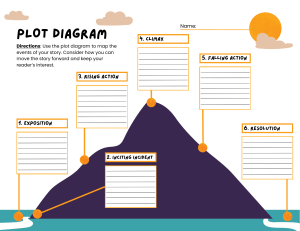
Elements of a Narrative Setting: The setting of a story is where and when the author decides to write the story. It is the time and it describes where the events take place (EX city, country/farm, neighborhood). It can contribute to the mood of the story and it helps create mental pictures in the minds of the reader. The author uses descriptive words and pictures to convey the setting. Theme: The theme of the story is the point of the story or the moral. It tells the reader why the story was written and what we can learn from life. Point of View: The point of view tells the reader who is telling the story. Sometimes, it is in first person (main character). This means that an “I” is telling the story about something that happened to him or her. The “I” is the person the author has created to tell the story. Other times, authors use third person (narrator) where the person is looking at the story from the outside. The third party voice of the narrator is not the voice of one of the characters. It is an “all knowing” voice who can see what is happening to different characters and what they see, know, and feel. The last POV is called the second POV and it uses the pronoun “you” to address the reader. This POV implies that the reader is a character in the story and the events are happening to them. Character: The character in a story is created by the author and it can be a person, animal or creature. As readers, we understand what the character is like by what they say (dialogue) and how they say it, what others say about them, how they act and what the character desires. The protagonist is the main character in the story. The antagonist is the character who opposes the protagonist. Conflict: Conflict in a story involves “the meeting of and struggle between opposing forces”. It can involve people against or vs. people, person vs. nature, a person vs. him or herself, a person vs. society or a person vs. technology. Resolution: The resolution is the part of the story's plot where the main problem is resolved or worked out. The resolution occurs after the falling action and is typically where the story ends. Another term for the resolution is "dénouement," which comes from the French term dénoué, meaning "to untie." Plot: The plot is the storyline. It is what happens or the sequence of events in the story. The plot starts with an introduction (and situation), has rising action (a conflict or complication), a climax, falling action and a conclusion/ resolution.