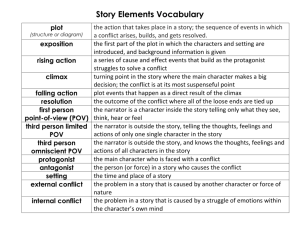
Narrative Elements Parts of a Story Narrative (story) elements (parts) are the various parts that most stories have. Some elements will play a major role in a story while others will be relatively minor. Stories could be novels, short stories, and plays. But they can also be movies, TV shows, gossip. Stories are a fundamental way we share knowledge and learn about the world and about ourselves. Setting Setting refers to the time and place that the story occurs. The place may be real or imagined. The time may be a time period (past, present, future), time of year (season), or time of day (dawn, morning, afternoon, evening, night). Plot Plot refers to the events that happen in the story from beginning to end. Most stories have a beginning, middle, and end (but not necessarily in that order). If the events are written in order, it is linear. If the events are not in order, it is non-linear. The plot may involve multiple scenes or episodes. Character 1 A character is a “person” in the story (even if he/she is not a human being eg. a robot, animal, fairy, sponge – they act and behave as humans). The main character is called the protagonist. The reader sympathizes with the protagonist (not all protagonists are “good” people). The character that opposes the protagonist is the antagonist. A character that changes (for better or for worse) during the story is called “dynamic”. A character that does not change is called “static”. Character 2 When a character is described in multiple and complex ways and made to feel like a real person he/she is considered “round”. A character that one-dimensional and only serves one purpose is considered “flat”. Characterizat ion Characterization refers to the ways the author reveals who the character is. They are: the character’s words, appearance, actions, thoughts, and reputation (what others say about him). Based on characterization, the reader forms an impression or opinion of the character. Conflict Conflict is the struggle between two forces. Conflict is an essential element to a story. The conflict may be: • Person vs person (external) • Person vs self (internal) • Person vs. nature • Person vs society • Person vs. supernatural Suspense Suspense is when the author creates the feeling of fear, anxiety, apprehension, excitement in the reader. The reader wants to know what the outcome will be. Atomosphe re Atmosphere (also called mood) is the general emotions or feelings that the story creates for the reader. This may be created by the weather, the events or character description, and various details. The atmosphere may be tense, light-hearted, etc. Point of View The Point of View (POV) is the perspective of the narrator (the person who tells the story). It may be first person, second person, or third person. For third person there is Omniscient POV (the narrator knows everything), and Limited Omniscient POV (the narrator does not know the thoughts of characters). 1st person: I went into the classroom. 2nd person: You went into the classroom. 3rd person (Omniscient): She went into the classroom filled with the anticipation of learning. 3rd person (Limited): She went into the classroom. Foreshado w Foreshadowing refers to when the author gives a hint or clue at the beginning of the story of what will happen later in the story. A symbol is an object or action that represents a larger abstract idea. Symbol Examples of symbolic objects are a dove (peace) and a heart (love). Examples of symbolic actions are kneeling (submission or deference) and standing with your hand over your heart (respect or loyalty). Personification refers to giving human qualities to inanimate objects or things. Personificati on Examples include: • Lightning danced across the night sky. • My alarm clock yells at me to wake up every morning. • I heard the last piece of pie calling my name. Image An image is when something is vividly described with various sensory details. The description is so powerful that it stands out for the reader. Images help the reader’s imagination to envision the characters, the setting, and/or the scene. Figurative Language Figurative language is when the author uses language that is not literal. It is comparative. The 2 main types are: • Metaphors: “All the world’s a stage. And all the men and women merely players” (comparing live theatre to life and how we all play a part) • Similes: “Life is like a box of chocolates” (a comparison that uses like or as) Theme is the main idea the author is conveying in a story. The theme is always related to human nature (how people live, what we desire, fear, search for, etc.). Stories are about a general topic. The theme is what the story suggests or shows about the topic. Theme Romeo and Juliet is a story about love (general topic). It shows how when people are in love they often follow their emotions more than their reason and how this causes problems (theme).