Treag All
advertisement

The Treag of Versailles
June. 1919
1. Germany is to give up about 70,000 sq.km.Of land and lose
about 8 million people. Land to be given to France, Denmark
and Poland
2. All profits from Germany's westem coal mines to go to France
3. Germany to give up all overseas colonies and trading rights in
foreign countries.
4. No German na\\J, air force. Army must be no larger than
100,000 men.
5. German factories to produce goods such
cars for the Allies free of charge.
as
machinery and rail
6. Germany to have no defenses along its border with France or
Belgium
7. About $33 Billion to be paid to the Allies in ,.reparations"
8. Included the "War Guilt Clause,,..*The AIIied and associated
governments declare, and Germany accepts the responsibility
for all the loss and damage saffered by the Altied ind
associated governments ss a consequence of the war imposed
upon them by the aggression of Germany and her alliei,
9. Many other sections (total 440 articles)
10.
League of Nations (U.N)
- Germany NOT a member!
Signed (incl. Germany) on June
Effective: January 10, 1920.
23,l9lg.
Name
Date
Article 51.
The territories which were ceded to Germany in 1871 lAlsaceLorrianel, are restored to French sovereignty....
Article
Germany renounces . . . all Iher] rights and titles over Iher] overseas
possessrons.,..
9.
1
1
1
59.
The German military forces shall be demobilized and reduced. . .
1
60.
By . . . March 31, 1920, the German Army must not . . . exceed one
hundred thousand men, including officers. . . . The Army shall be
devoted exclusively to the maintenance of order within the territory
and to the control of the frontiers. . .
Article 198.
The armed forces of Germany must not include any military naval or
Article
Article
.
airforces....
Article
231
.
The Allied ... Governmelts affirm and Germany accepts the responsibility of Germany and Iher] Allies for causing allthe loss and
damage to which the Allied and Associated Governments and their
nationals have been subjected as a consequence of the war impoled
upon them by the aggression of Germany and lhed allies.
Souf<e: Ihe Treaty af Vertailles and After (U.5. Government Prlnting Ofli(e).
Pre5ented by the Allier to Germany May 7, 1919, at Versailler,and rigned lune 28, 1919.
1. ldentify the terms of the Treaty o;f Versailles that you think were most humiliating to Germany. Explain your choices.
Choose any three of the terms listed above. Why would the Allies believe each
of these terms was necessary? Why would the Germans believe each of th ese
terms would be too damaging?
copyright
o
2001 cage iFducational PUblishing
279
After the Fighring
FICUR-E
An armistice does not ensure peace.
If is simply an
agreemenr to a ceasefire, and
war can be resumed if no
lasting solution is found. The
terms of the armisrice tha
ended the First World lvar were
very harsh toward the
Cermans. The Allies intended
to make it impossible for
Germany to resume the lvar
before the terms of a full
peace treary could be drafted.
In early 1919, Allied delegates
met at Versailles,
outside Paris, to draw up the peace
treary Canada was
grven the right to be present ar
rhe paris peace
Conference as a separate de)egation
from the Brirish.
nowever, the Brirish. French. and
Americans dominated, and they were responsible
for the content of the
treafy. The Germans were not allowed
to send delegates
to.the conference. They rvere forced
to agree to the
Allies' demands, under
the threat that the war
would be resumed if they
did not. They signed the
I-32
Signing ceremony of the Treary of Versat
es, Igt9
.
.
.
.
Germany was to evd6uate all territories
captured during the war and surrender
all
ItS OVerse as c olo nies.
.
.
ln addition to the termf of the armistice:
.
rreiman trodps were required to
withdraw
10 kilometres east of the Rhine
River.
They were to leave behind all
their artillery
machine guns, trucks, and other equipmeirt
They were req0ired to surrendertheir
and all their merchant
.
Treary of Versailles under
protest on June 23, 19 t9.
rasr oi these left in 1929).
.
.
naw
Germany was to compensate tha Allies
for .
war damages.
.
bermany was to surrender most of its
raiiway rolling stock and locomotives to
the
Fren c h and I elgians.
.
resutt, many German civilians
starved to
death during the winter of lglg_.1919.)
The German army was reduced
in size
100 000 people, and conscription
sh io s.
The Allied blockade of Germany
was to continue until a peace treaty was signed. (As
a
Germany had to evacuate the
Rhineland
(Germany west of the
Rhine River), which was
demiircarizeo and occupi-ed by Allied
troops (the
.
'
to
was abolished.
The Germans were forbidden to maintain
an air
force or to build submarines and tanks.
The German Navy was reduced from
23 battleshipsto 6 (all buittbefore '|905).
Germany was forced to admit responsibility
for
causing the war (the War Guilt Clause)..
Germanywas required to pay damages (reparations) to the Allies in the amount of
f6600 million
($30 billion).*
Nots that PresidBnt Wilson,s Fo!rtesn points
nads no mention
of war guih or reoarations.
'^-" --;".,1
F&i
:-
tsEMND
dLx
UNION OF
sovtFI s0ctAUsr
fiEPUBUCS
lussR)
POLANO
IIIGMBOUS6
!\.t-
PORT!/6ALT
+ (
f:)
,(l
SPAIN
c
f,
FrcuRE
PERSIA {lNAN)
l-33
Europe in 1922. What changes had occuned since 1914?
The Leagrre of Nations
ne of the terms of President Wilson's Fourteen
roints and of the Treaty ofVersailles was the creon of an organization that would preserve
among nations and improve the quality of
^reace
life for all the peoples of the world. This organization, the League of Nations, came into being in
1.920. Headquartered in Geneva, in neutral
Switzerland, it hegEn with 42 merther narions.
Py 1939, i;renbership rvas 63.
During the 1920s, rhe League helped ro
resolve several disputes befween member
nations. However, it was hampered in its lvork
because some major narions, including rhe
United States, did not belong. In addition, some
nations that did belong were not prepared to use
troops to compel other countries to obev resolutions passed by the League.
During the t930s, internationa.i aggression
mounted, and it became clear that the League was
not capable ofpreventing a second global conflict.
FrcuRE
l-34
First in{ormal meeting of the League of Nations in
G eneva, Switzerland, 1920
Aft.' th.
1.
Fightingr The Tr.ate uf Versaill.t,17l?
Whot is on ormisiice?
2. What were the gools of the Allies during the tolks at the Paris Peoce Conferznce?
3. Which countries dominoted fhe Conference? What were their gools?
(i)
(tt
)
(iii)
(Do you know who these men ore?)
4. Under whot conditions did the 6errnons sign the Treoty of Versoilles? Do you think thot
this wos foirZ
5. Look ot sotne of the terms of the Treoty of Versoilles. Which 3 terrns do vou think ore
the rrost hurnilioting to Germony? Why?
6. How wos Conoda involved in the Treoty of Versoilles2
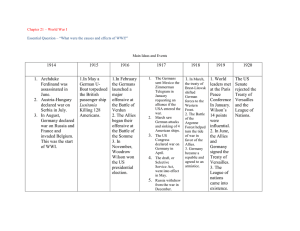
THE END OF WORLD WAR I AND THE TREAry OF VERSAILLES
World War One ended at 11:00am on November 1 l, 19i 8 (1 1'n hour of the l1'n day of
the 11th month). By the end of the r.var 66,000 Canadian soldiers had been killed and
another I 73,000 wounded.
On June 28, 1919, most of the countries r.vho had tbught in World War One signed the
Treaty of Versailles. Many people thought that this peace treaty r.vould prevent futurc
wars. They believed that people and countries would leam from their mistakes and avoid
the horrors of another world war.
The countries which won the war, especially France wanted revenge on Gennany. They
wanted to teach Germany a lesson. They thought that Germany should be forced to take
blame for World War I. They insisted that Germany agree to pay back all the money
which the rvinners had spent on the war - a total of $3 5,000,000,000 ! Gemany was also
lorced to give up its colonies (countries it owned overseas) and some of its lands.
Belgium, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Denmark and France received German land which
contained about 6.500.000 German citizens.
The Austro-Hungarian Empire was divided up by the wimers of the war and Communist
Russia was punished for leaving the war in 1917. Several new countries like Poiand and
Czechoslovakia were created fiom the lands taken away from Germany, Austira-Hungary
and Russia.
The Treaty of Versailles humiliated the losers. When Germany tried to protest against the
conditions of the treaty, the winners of World War I threatened to invade Cermany.
Germany was lbrced to sign the treaty but the shame Germany felt would never be
forgotten by the German people.
Also an interesting note - the Italian people began the war as part of the Triple Alliance
(Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy) but the day after the war began, they switched side
to fight with the Allies. Even though the Italians fought on the side ofthe Allies during
the remainder of the war, they were not very well rewarded for their work by the Treaty
of Versailles. Italy received very little new territory as a reward at the peace conference.
This angered manlr Italians.
When Canada sigred the Treaty of Versailles in 1919, she also became part of the League
of Nations a group formed to stop fufure wars. Canadians had made a huge contribution
to the war effort. Besides all of the money Canada had spent on the war, 66,000
Canadians had iost their lives. The soldiers who did retum believed they had fought to
make the world 'safe for democracy'. They hoped that World War I would be the "war to
end all wars." However, the truth was that there was less chance of permanent peace and
democracy in the world betbre the slaughter or World War I had begun. They rvould
never be able to return to those leisurely days at the turn of the century. The life they had
kno',vn was gone forever.
THE END OF WORLD WAR I AND THE TREAry OF VERsAILLES
1.
World War One ended on
2.
How many Canadians rvere killed
3.
What was the name of the Peace Treatv that ended the War?
4.
What was the treaty meant to do
wounded
5. What did France want at the end ofthe war?
6. What countries received land fiom Geramny?
7. What happened to Austria-Hungary?
What happened to Russia?
8.
\\&at new countries rvere created bv the Treatv?
9. How much money did Germany have to pay the winners?
10.
True False
The treaty humiliated the Germany people.
1l.
Tme False
Canada signed the peace Treaty?
12. What organization rvas formed after WWI?
What was this organization supposed to prevent?