Document 14452478
advertisement

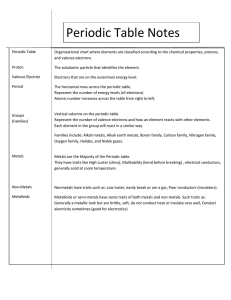
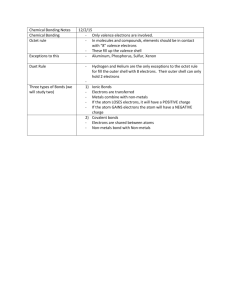
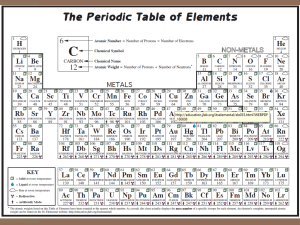
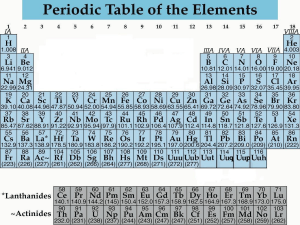
•Structured arrangement of elements that help us to explain and predict physical and chemical properties •Metals are located on the left side •Non-metals are located on the right side (exception: H) •Metalloids are found on either side of the staircase (exception: Al) Property Metals Non-Metals Example nickel, Ni bromine, Br State mostly solid solid, liquid or gas Lustre shiny dull Malleability generally malleable brittle (if solid) Conductivity conductors insulators Sodium, Na Carbon, C Period: row of elements on the periodic table Indicate the number of shells Group: columns on the periodic table with similar properties Indicate the number of valence electrons Group 1 elements (exception: H); e.g. Na, Li, K Highly reactive metals Like to form ionic compounds with group 17 non-metals Group 2 elements e.g. Mg, Ca, Ba Fairly reactive metals Group 17 elements e.g. F, Cl, Br Highly reactive non-metals Group 18 elements e.g. He, Ne, Ar Stable, unreactive elements Recall: The first orbit can hold 2 electrons The second and third orbits can hold a maximum of 8 electrons ▪ Atomic number = # of protons ▪ # protons = # electrons (in a neutral atom) ▪ Atomic mass – Atomic Number = # neutrons • Simplified drawing representing the valence electrons • Draw the element’s symbol and surround its 4 sides with dots which represent the valence electrons Recall: Group # = # of valence electrons H F Hydrogen Fluorine