Middle Ages
advertisement

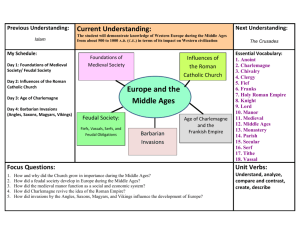
Middle Ages Post-Classical Europe • Known as __________ Ages – • ____________ Period Europe viewed as_____________ by other peoples of the world – Less ______________ and _________________ development Early Post-Classical Period • • Many problems in the early years of the post-classical period – Viking _____________ – Weak ____________ due to decentralized _________________ – ____________________ – ________ agricultural productivity Economic Activity: – – ________________ farming common • Many people lived as _____________ on large manors owned by a wealthier ___________________ • Serfs had difficult lives, but were not ______________ Low agricultural productivity • • Inefficient __________ and farming _______________ made agriculture difficult Government: – ______________ government – __________________ was most common political and economic arrangement • ______________ and serfs worked on agricultural estates owned by landlords • Exchanged part of their ___________ and labor for _______________ – Very few ____________ kingdoms developed • • Charlemagne (________________________) – • 8th century: Established empire in _______________, ______________, and ______________________ Achievements under Charlemagne – Promoted__________________ • • __________ copied works from the past Empire fell apart shortly after Charlemagne’s death (_______) – • Exception was _____________________short-lived empire Split into ___ kingdoms, which developed ______________ from each other Fall of Charlemagne’s Empire set stage for further __________________ in Western Europe – Fragmented into _______________ kingdoms, which would later become _____________ – Regional _____________ emerged to further ______________ the people • Most based on ___________ (known as Romantic Languages), others based on _______________ languages Religion • _________________ was sole unifying force in Western Europe – Catholicism – ____________ (in Rome) center of religious _________________ – Local ___________ – ____________ work – Monasteries and convents • ___________ and __________ served as religious ______________ to other Europeans • Promoted __________________ • __________ became the language of _______________ people and church _____________ in Europe – Most people unable to __________, ___________, or understand Latin Slow Changes after 900 C.E. • In _______ Century, Europe did experience small developmental changes – – New______________ techniques and technology made farming more productive • Moldboard _________ • Landowners began to accumulate more ____________ through sale of ag. ___________________ Population growth • – Able to ___________ more people ___________________ increased • Cities became _______________ centers • – Still small in comparison to ____________ East Growth in education • _________________ educated those who were destined for the Church • ________________ grew in cities – _____________ conversions to Christianity led to fewer ____________ and invasions – Europe began to engage in more long-distance trade • New crops and technologies Governmental Changes • _________________ emerged as the dominant _____________ system – Began as localized agreements, grew into feudal _____________ – System where____________ (military elites) exchange ____________ and ___________for _____________(manors) • _____________: lesser lords who swear ______________ to a more powerful lord (king) – • Loyalty in exchange for land (_________) Manors were worked by serfs and/or freed peasants – Exchanged labor and commodities for ______________- Knights • Armored ___________ of the middle ages • Use of ____________ in warfare – • Adopted stirrup from Central Asian ______________ Armor – Started out as open-faced _____________ & long, metal studded shirts (____________) – Evolved into helmet with small _________ and metal ____________ Governmental Developments • Overtime, kings used feudalism to buildup their own _____________ • Examples of Governmental Development: – ______________ Family in France: • – England: • • Powerbase near ____________, spread influence outward to create a feudal kingdom William the Conqueror (_____________________) invaded England and abruptly established a feudal kingdom Europe’s political development was hindered by several factors – ________________ limited power of many kings • – _________ directly controlled central ____________ • – Became involved in _______________ Indirectly many other areas of ____________ Feudal Kingdoms ___________ each other • France and England ______________ • • In early part of Middle Ages, ______________ were also restricted by the ideas of: – Limited Government • – ___________________ (1215) Representative Government • 1265: Introduction on ____________________: elected legislatures that are ____________________ of the people • • The _______________ Years War _______________ developed the strongest Parliamentarian system People ______________ giving the monarch too much ______________. Expansion of European Influence • Population_____________ and economic _________________ led to an increase in European expansion – Expand into ___________ Europe – _________________ in Spain • Efforts to remove _______________ influence in Spain – Completed in ________ – Portugal emerged as a _______________ power in Mediterranean and began to increase exploration along coast of _____________ – Spain created after marriage of _____________ and _______________ » – Alliance between ____________ and _______________ Viking exploration in ______________, ______________, and Hudson Bay area of _________________ Crusades • Series of ______________ wars between ______________ and ______________ – • • Fight for control of _______________ and access to riches and trade in __________________ First Crusade in 1095 (request of _______________) – Promised _______________ for Crusaders – Gained control of __________________, later lost the city when _____________ rallied under the leadership of _____________ in 12th century Impact of the Crusades – showed the west’s ___________________ toward the rest of the ________________ – Exposed Europe to new _________ and __________________ Culture of the Middle Ages • ____________ dominated culture • Conflict between ________ and____________ – _____________: study of religion – Growth in ___________ education in later years • • • BUT Minimal _____________ discovery Art was used to ____________ God – _________images, ___________ glass windows with ________________ scenes – ____________ Architecture- buildings appeared to be reaching to the ____________ Much of _____________ done in Latin with religious topics BUT – Some began to write in the___________________(language spoken by common people) about ____________ topics • Poems about _________, _______________, and court life were common Economy • • 90% of population was __________ – Most people ___________ or ____________ – Made living through _________________ _______________ growth saw increase of ____________ – Became cultural and _______________ centers – Increase in ___________ labor • – Skilled labor usually restricted to members of ______________ Trade picked up (particularly in __________ and areas near coast) • Merchants became huge source of _____________, made loans to ____________ • _________________ with Church because Church frowned upon charging interest on loans and feared money would ______________ people – • ______________ became major money lenders b/c their religion did not __________________ charging interest (usury) Europe also saw development in certain industries – ____________ increased and Europe was able to access metals for __________ and _____________ making – European’s harnessed the power of _____________ from its many rivers and streams • Water Wheels used in __________ to help grind grain and perform other tasks Urbanization • As populations and cities grew, the economy began to develop more ______________ • Problems of Urbanization and Economic Development – Environmental ________________ • – ________________, pollution of streams, lack of ______________ _____________ Black Death • ____________Plague – Caused by bacteria, transmitted by _________ and _________ • – _______________ disease • • __________ treated with antibiotics Boils, blacks spots on skin, foul body odor Impact – Killed ______ of European population – Skilled labor more expensive due to ________ shortages – Peasant _____________, led to swift decline in serfdom as peasants and serfs _________ away from their manors – ___________in cities Government Structure in Late Middle Ages • Toward the end of the Middle Ages, _____________ monarchies began to _____________ in power – Feudalism ______________ and aristocrats lost much of their power • New military _____________reduced the need for knights – • ________________and artillery (cannons),____________ and ___________became major part of military Kings began to ___________ military personnel rather than depend on the ________________ – Paid for with __________ from bankers/businessmen and with new _________ that were collected on merchants and land Conclusion • Middle Ages were a time of _________________ in Western Europe. – _______________ in some areas while still _____________________ in others – _________________ innovation in mining, milling, and waterpower BUT still _______________food production – ___________ advances BUT at cost of more frequent _______ and ___________ – _________ increased and helped improve the European economy BUT gap between ________ and ___________ still wide – ____________ growth offset by ______________