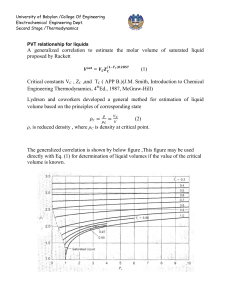
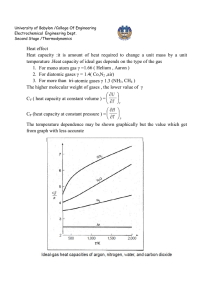
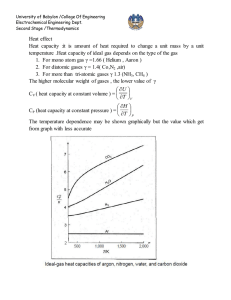
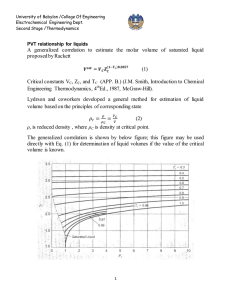
University of Babylon /College Of Engineering Electrochemical Engineering Dept. Second Stage /Thermodynamics
advertisement

University of Babylon /College Of Engineering Electrochemical Engineering Dept. Second Stage /Thermodynamics Equation of state PV=nRT is the simplest equation of state and is called ideal gas equation Virial EQUATIONS OF STATE For an isothermal such as T 1 as pressure increase , volume decrease , thus PV product for gas or vapor should be more nearly constant and this lead to suggest that PV along isotherm can be represented as a power series equation , this called Virial equation state PV 1 BP C P 2 DP 3 ..... RT PV B C D z 1 2 3 .... RT V V V B B RT C B2 C ( RT ) 2 z D D 3BC 2 B 2 ( RT ) 3 B,B are second Virial coefficients ,C,C are third Virial coefficients and so on. Values of C, like those of B, depend on the gas and , temperature. The below figure shows a compressibility-factor graph for methane. Values of the compressibility factor Z (as calculated from P VT data for methane by the defining equation Z = P V / RT) are plotted vs. pressure for various constant temperatures. 1 University of Babylon /College Of Engineering Electrochemical Engineering Dept. Second Stage /Thermodynamics all isotherms originate at value z=1 for P =0. the isotherms are nearly straight at low pressure . Thus the equation of the tangent lines is z = 1+ B P dz B 2C P 3DP 3 .... dP dz B slop dP P 0 z PV BP 1 RT RT This equation satisfactorily the PVT behavior of many vapors at subcritical temperature up to pressure of about 5 bar. for pressure the range applicability of Eq. but below the critical pressure, the Virial equation truncated to three terms often provides excellent results. PV B C z 1 2 RT V V 2 University of Babylon /College Of Engineering Electrochemical Engineering Dept. Second Stage /Thermodynamics This equation can be solved directly for pressure, but is cubic in volume. Solution for V is easily done by an iterative scheme with a computer. The effect of temperature on C and B for Nitrogen are illustrated on below figure 3