5-51 heat transfer are to be determined.
advertisement

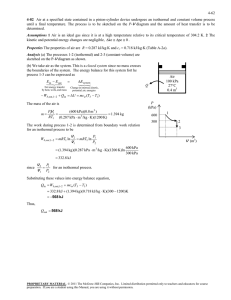
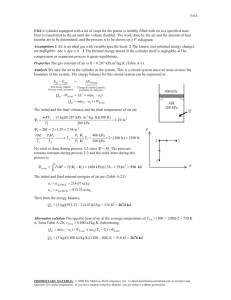
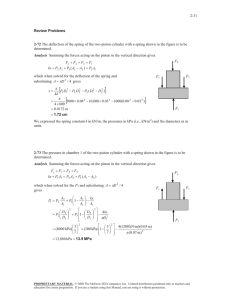
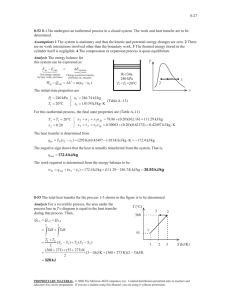
5-51 5-72 Air in a closed system undergoes an isothermal process. The initial volume, the work done, and the heat transfer are to be determined. Assumptions 1 Air is an ideal gas since it is at a high temperature and low pressure relative to its critical point values of 132.5 K and 3.77 MPa. 2 The kinetic and potential energy changes are negligible, 'ke # 'pe # 0 . 3 Constant specific heats can be used for air. Properties The gas constant of air is R = 0.287 kJ/kgK (Table A-1). Analysis We take the air as the system. This is a closed system since no mass crosses the boundaries of the system. The energy balance for this system can be expressed as E E in out Net energy transfer by heat, work, and mass 'E system Change in internal, kinetic, potential, etc. energies Qin Wb,out 'U Qin Wb,out 0 Qin mcv (T2 T1 ) (since T1 Air 600 kPa 200°C T2 ) Wb,out Q The initial volume is V1 (2 kg)(0.287 kPa m 3 /kg K)(473 K) 600 kPa mRT1 P1 0.4525 m 3 Using the boundary work relation for the isothermal process of an ideal gas gives 2 Wb,out ³ 2 m Pdv mRT 1 dv ³v 1 mRT ln v2 v1 mRT ln (2 kg)(0.287 kPa m 3 /kg K)(473 K)ln P1 P2 600 kPa 80 kPa 547.1 kJ From energy balance equation, Qin Wb,out 547.1 kJ PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Limited distribution permitted only to teachers and educators for course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.