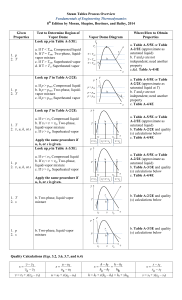
4-32 to be determined. m
advertisement
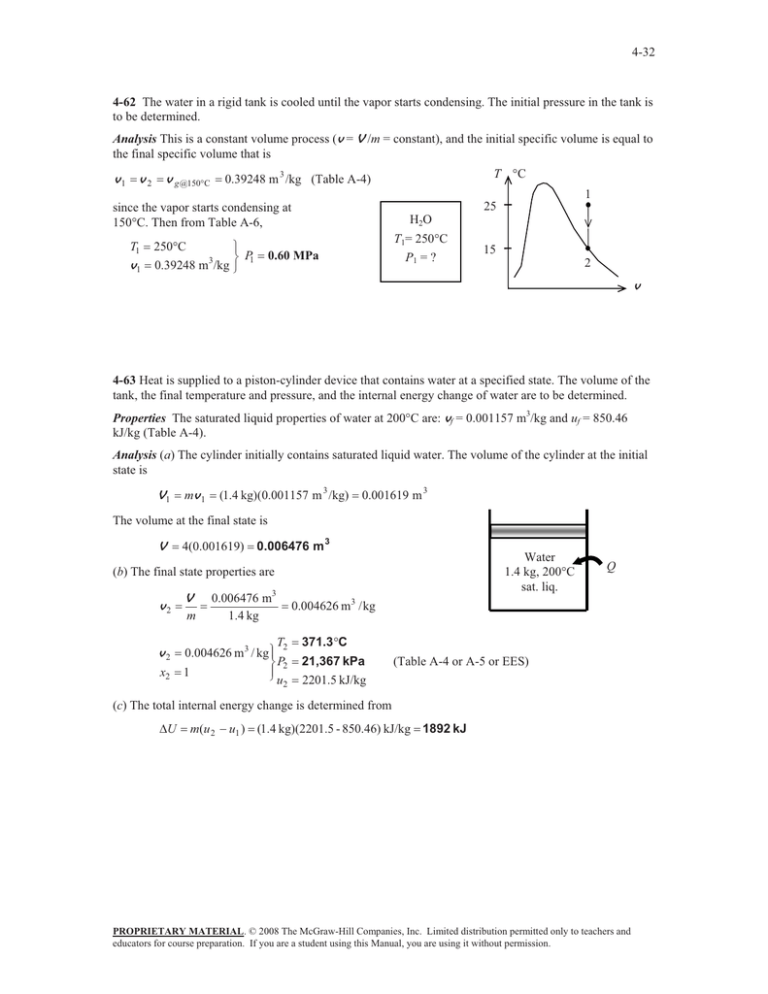
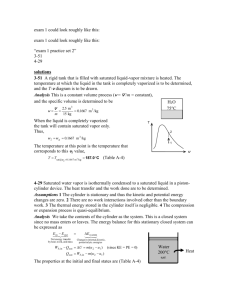
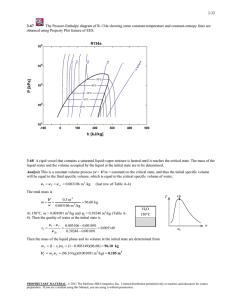
4-32 4-62 The water in a rigid tank is cooled until the vapor starts condensing. The initial pressure in the tank is to be determined. Analysis This is a constant volume process (v = V /m = constant), and the initial specific volume is equal to the final specific volume that is v1 v 2 v g @150qC T qC 0.39248 m 3 /kg (Table A-4) 1 25 since the vapor starts condensing at 150qC. Then from Table A-6, T1 v1 250qC ½ ¾ P 0.39248 m3/kg ¿ 1 H2O T1= 250qC P1 = ? 0.60 MPa 15 2 v 4-63 Heat is supplied to a piston-cylinder device that contains water at a specified state. The volume of the tank, the final temperature and pressure, and the internal energy change of water are to be determined. Properties The saturated liquid properties of water at 200qC are: vf = 0.001157 m3/kg and uf = 850.46 kJ/kg (Table A-4). Analysis (a) The cylinder initially contains saturated liquid water. The volume of the cylinder at the initial state is V1 mv 1 (1.4 kg)(0.001157 m 3 /kg) 0.001619 m 3 The volume at the final state is V 4(0.001619) 0.006476 m 3 Water 1.4 kg, 200°C sat. liq. (b) The final state properties are v2 v2 x2 V m 0.006476 m3 1.4 kg T2 0.004626 m3 / kg ½° ¾ P2 °¿ 1 u2 Q 0.004626 m3 / kg 371.3qC 21,367 kPa 2201.5 kJ/kg (Table A-4 or A-5 or EES) (c) The total internal energy change is determined from 'U m(u 2 u1 ) (1.4 kg)(2201.5 - 850.46) kJ/kg 1892 kJ PROPRIETARY MATERIAL. © 2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Limited distribution permitted only to teachers and educators for course preparation. If you are a student using this Manual, you are using it without permission.