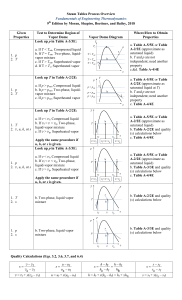
Steam Tables Process Overview Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics th 8 Edition by Moran, Shapiro, Boettner, and Bailey, 2014 Given Properties Test to Determine Region of Vapor Dome Look up p in Table A-3/3E: Vapor Dome Diagram T Tc a. If T < Tsat, Compressed liquid b. If T = Tsat, Two-phase, liquidvapor mixture c. If T > Tsat, Superheated vapor d. If T > Tc, Superheated vapor 1. p 2. T ● p c • T > Tsat b T = Tsat T < Tsat a • v Look up T in Table A-2/2E: a. If p > psat, Compressed liquid b. It p = psat, Two-phase, liquidvapor mixture c. If p < psat, Superheated vapor 1. p 2. T T p a p > psat • b p = psat p < psat c • v Look up T in Table A-2/2E: 1. T 2. v, u, h, or s a. If v < vf, Compressed liquid b. If vf < v < vg, Two-phase, liquid-vapor mixture c. If v > vg, Superheated vapor 1. p 2. v, u, h, or s a. If v < vf, Compressed liquid b. If vf < v < vg, Two-phase, liquid-vapor mixture c. If v > vg, Superheated vapor a b T • c • • v<vf v vg vf<v<vg v>vg a b c p • • • v<vf vg vf<v<vg v T b vf p 1. p 2. x b. Two-phase, liquid vapor mixture a. Table A-5/5E or Table A-2/2E (approximate as saturated liquid) b. Table A-3/3E and quality (x) calculations below c. Table A-4/4E p x b. Two-phase, liquid vapor mixture a. Table A-5/5E or Table A-2/2E (approximate as saturated liquid) b. Table A-2/2E and quality (x) calculations below c. Table A-4/4E v>vg T 1. T 2. x a. Table A-5/5E or Table A-2/2E (approximate as saturated liquid at T) b. T and p are not independent; need another property c. Table A-4/4E p vf Apply the same procedure if u, h, or s is given. a. Table A-5/5E or Table A-2/2E (approximate as saturated liquid) b. T and p are not independent; need another property c.&d. Table A-4/4E T vf Apply the same procedure if u, h, or s is given. Look up p in Table A-3/3E: Where/How to Obtain Properties b. Table A-2/2E and quality (x) calculations below • v vg v T b. Table A-3/3E and quality (x) calculations below x p b vf • v vg v Quality Calculations (Eqs. 3.2, 3.6, 3.7, and 6.4) x v vf vg vf v = vf + x(vg – vf) x u uf ug uf u = uf + x(ug – uf) x h hf h hf hg hf hfg h = hf + x(hg – hf) = hf + xhfg x s sf sg sf s = sf + x(sg – sf)