A Review of US History for the EOC
advertisement

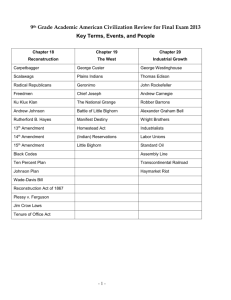
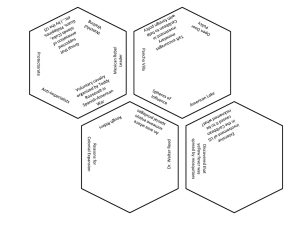
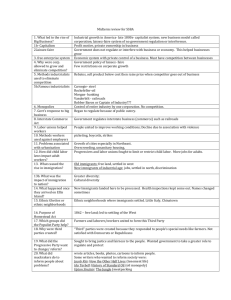
A Review of US History for the EOC MRS. PEYTON & MR. HART (BUT MOSTLY LOGAN NAPIER AND IN NO WAY AT ALL DID EMILY BALL HELP) George W Bush Deregulation: an economic policy in which government loosens restrictions on corporations Deficit Spending When a government spends more money than it brings in Patriot Act Government's response to 9/11, provided for increased surveillance and is seen as a loss of freedoms/privacy rights United States aid to Afghanistan in 1980's Aided them to help defend against a Soviet invasion of their country Industrial Revolution The modern day development of information technology has had an impact similar to it. North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) The trade agreement between Canada, U.S. and Mexico created a potential for job losses, wage cuts, and environmental abuses. President Reagan's Foreign Policy (1980's) The path to peace lies in America's strength and willingness to assist anticommunist forces throughout the world, BY GOD. Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev began 2 new policies Glasnost: an openness (transparency with the government) Perestroika: restructuring (more capitalist) President Carter's difficulties (late '70's): Rising unemployment Iranian hostage crisis Energy crisis (Middle East controlled oil, therefore prices) Equal Rights Amendment (ERA) for women's equality Social conservatives affiliated with several Christian denominations led opposition to the ERA and emerged as a powerful political force. Flower Power Image It symbolizes the tension between nonviolent civil disobedience and the threat of force. Détente: an easing of tension Nixon's China Official visit to the People's Republic of recognition of China & opening diplomatic relations César Chávez Known for leadership on labor issues for migrant workers. Civil Rights tactics Martin Luther King, Jr. & the Southern Christian Leadership Conference: Nonviolent or Civil Disobedience Malcolm X: Nation of Islam supported blacks defending themselves Cuban Missile Crisis 1962 Soviets intend to put missiles on Cuba JFK establishes a quarantine Khrushchev removes US pledges not to invade; missiles in Turkey removed WWIII averted! It led to improved communications between the two countries Rock and Roll music Broke down racial barriers It appealed to both races because it developed out of both musical traditions. Encouraged protests, challenging authority Domino Theory If one country falls to communism, many more will GI Bill 1944 Allowed Helped veterans to attend college transition veterans back into the workforce Nuremberg Trials WWII victors put Nazi officials on trial for crimes against humanity Revealed details of the Holocaust Rosie the Riveter Famous poster symbolizing women in the workforce for WWII Battle of Midway First significant naval success the US had over Japan Marked a turning point in the Pacific Theater WWII rationing & price controls The U.S. government introduced this to limit individuals usage of certain necessary items (food, gas, metals, etc.) vital to the war effort Result was that people had money to spend after the war was over and goods to spend them on Pearl Harbor December 7, 1941 We declare war on Japan Germany and Italy then declare war on us Internment camps Reaction to Pearl Harbor, Executive Order 9066 calls for over 100,000 Japanese Americans to be rounded up and put into camps out West Challenged under Korematsu v. U.S., but the Supreme Court upholds the governments actions Onset of the Great Depression Overproduction in agriculture and industry High tariffs and war debts Unequal distribution of wealth Speculation on the stock market Installment plans increased consumer debt Stock Market Crash Charles Lindbergh's flight across the Atlantic Ocean A hero of the 1920s, Lindbergh solo flight in "The Spirit of St. Louis" symbolized the tremendous possibilities of air travel Roaring Twenties Flapper What additional factor contributed to the 1929 stock market crash? Agricultural problems (overproduction) Mass production—Consumerism, advertising, installment plan Red Scare & Palmer Raids Plessy v. Ferguson Upheld the separate but equal law and spread to north not only in south Sacco and Vanzetti Two Italian immigrants are accused of theft and murder Though evidence is unclear, public opinion quickly turns against them because they are Italian and anarchists They are found guilty and executed The case symbolizes the growing paranoia Americans have of immigrants and the fear of communism and anarchism during the 1920s Scopes "Monkey" Trial John T. Scopes teaches evolution in a Dayton, TN classroom Though he loses the case, it symbolizes the clash in the 1920s between the forces of science/change/urban values and the more traditional/rural/conservative values Korematsu v. U.S. President Wilson's Fourteen Points To provide a plan for just and lasting peace to end WWI Included the League of Nations Prior to U.S. entry into WWI, what factor most challenged its neutrality Germany's unrestricted submarine warfare But remember: Lusitania sunk in 1915; we don't enter war until 1917 Triangle Shirtwaist Factory tragedy Fire in a clothing factory kills 145 in New York This exposes the widespread lack of safety precautions and poor working conditions in early 1900 factories President Taft's Dollar Diplomacy American foreign policy aimed at Latin America and East Asia by investing in those areas to create stability and promote U.S. commercial interests Upton Sinclair—muckrackers Muckrakers – term used in the Progressive Era for American journalists/writers who exposed the ills of society Upton Sinclair wrote, The Jungle – exposing the terrible conditions of workers in the meatpacking industry, as well as the unsanitary condition in which meat was handled Monroe Doctrine & Roosevelt Corollary Monroe Doctrine - U.S. foreign policy that opposed European nations intervening in the affairs of nations in the western hemisphere Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine – Latin American nations must keep order or the United States will come down and fix it for them President Theodore Roosevelt's trustbuster Roosevelt believed that business monopolies could potentially hurt the public interest However, he did distinguish between good and bad trusts, only going after the bad ones U.S. interests in China—Boxer Rebellion The Open Door policy attempted to secure for America the same power as European nations had to openly trade in China A group of Chinese (known as the Boxers) attempt to kick out all Westerners from China 1903 revolt in Central America— Panama Canal U.S. encouraged this revolt because the Colombian government refused to ratify an agreement allowing construction of the Panama Canal After we help Panama become a new country, we build the Panama Canal Philippines after the Spanish-American War President McKinley decided to keep control after the war to increase commercial opportunities for U.S. trade in Asia The Filipinos do not want this and then fight the United States We lose more soldiers here than during the Spanish-American War 1893 overthrow of Hawaiian government U.S. government participated in the removal of Queen Liliuokalani because of her attempt to reduce the political influence of American sugar planters Hawaii is then annexed and later becomes a state Pearl Harbor is here Alfred Thayer Mahan—The Influence of Sea Power Upon History Mahan said that a nation benefited from having a strong navy and the overseas bases needed to maintain it Important to America's expansion/imperialism in the late 1800s William Jennings Bryan's 1886 "Cross of Gold" Speech Main topic of this speech was changing the U.S. government's monetary policy by freely coining silver (both silver and gold would back U.S. dollars) This would put more money in circulation and help farmers (Populists) pay off their debts with cheaper money It would cause inflation Populist Party Political party made up primarily of farmers who wanted the government to regulate railroads and put more money in circulation Many of their ideas were later adopted by the Progressives Nativists Americans who supported only nativeborn citizens Nativists considered immigrants from southern and eastern Europe more difficult to assimilate into American culture than earlier immigrants John D. Rockefeller Reacts to Government Restrictions on their Businesses Placed his company under the controls of a board of trustees City Bosses and their Political Machines Kept control of the city governments by providing aid to citizens in exchange for their political support They controlled major cities Very much used the immigrant vote to stay in power Feminists in the Late-Nineteenth Century Feminists disagreed on the suffrage movements goals and tactics after women's suffrage was not included in the 15th admendment Policy towards American Indians After the Civil War Dawes Act: Apportionment individuals of tribal property to Wade Davis Bill Congress's It counter to Lincoln's 10% plan required a majority of Southerners to take an oath of loyalty to be admitted back into the Union 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendment 13th -- abolition of slavery 14th – citizenship to all born or naturalized the U.S.; citizens guaranteed due process of law and equal protection under the law 15th – cannot be denied the right to vote based on race Anaconda Plan The Union military strategy against the Confederacy to completely surround them so the South could not get access to supplies Underground Railroad Northern States Had What Advantages Over Southern States A more extensive railroad system More An industry established government Larger population Reform Movement Feminism During the Antebellum Period Involvement of women in a variety of reform movements Women were seen as more moral and virtuous, thus social reform were in their "sphere" Factory System With the introduction of the factory system. . . Women Textiles moved into factories were mass produced Peoples workdays were defined by the clock Dred Scott vs Sanford 1857 Supreme Court Case Issue: A black slave had been taken by his master into the Minnesota region, which, according to the Missouri Compromise, was a free territory Did residence in a free territory make him a free man? The Supreme Court said, "No." Black men were not citizens, they were property, and could not bring suit in Federal court Therefore slavery could exist anywhere Regional Economic Differences During the Mid-Nineteenth Century Northern Manufacturing, Shipping, Railroads Southern Agricultural, Slavery Northerners Strongly Object to the 1846 War With Mexico This war would open territory to expansion of slavery Temperance The drink is bad! The mid-1800's movement led by women to restrict alcohol Prohibition The 18th Amendment to the US Constitution (1920) It bans the manufacturing, distribution, and sale of alcoholic beverages Enforced by the Volstead Act Never completely ended alcohol use or abuse, but it did create new criminal activities such as bootlegging and speakeasies Repealed by the 21st Amendment Suffrage Seneca Falls & the Declaration of Sentiments (borrowed language from the Declaration of Independence) Goals: Right to Vote, Overcoming the "Cult of Domesticity" Leaders: Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Lucretia Mott National Women's Suffrage: 19th Amendment (1920) Louisiana Purchase Thomas Jefferson's expansion of American territory Eliminates French influence in America Manifest Destiny: Go West! American Expansionist Mindset, destined by God Brings about the Oregon Trail and exploration of the Northwest and West Coast Promoted by Land-hungry Americans American fears of British desire for land Merchants' desire of the Pacific Ocean for trade Democratic-minded people seeking to spread freedom, individualism Nationalists who sought America's greatness War of 1812 War between the US and Great Britain Causes: Britain's seizure of American ships and impressing American sailors American resentment of Britain American belief that Britain and Canada were arming Native Americans American ambitions to annex Canada and Florida War of 1812 Effects of the war: A tie that makes America feel good about itself! Native Americans lose, on their own vs. Americans Marbury vs Madison This 1803 case established the fundamental government principle of Judicial Review—role of the Supreme Court to interpret the constitutionality of laws First Continental Congress--1774 Addressed a "Declaration of Rights and Grievances" to King George III and voted to boycott British goods An attempt to reconcile with Britain and avoid war Lexington and Concord "The Shot heard Round the World" came from the Battles of Lexington and Concord These conflicts began the fight that led to the creation of the United States and inspired Revolutions elsewhere Shays' Rebellion Massachusetts farmers protest the way the government is treating them (throwing them in debtor's prison) Exposes the weakness of the Articles of Confederation and the need for a strong central gov't Bacon's Rebellion A poor backwoods population (many of them were former indentured servants) attack Jamestown, protesting that colonial gov't is not protecting them 1st colonial revolt Join or Die: Ben Franklin's political cartoon Used 1st in the French & Indian War to encourage colonial unity siding WITH the British against the French Used a 2nd time in the Revolution to promote colonial unity against British tyranny American Enlightenment Important Ideas that came from the Enlightenment Based Right on science and reason to explain the world of Revolution Life, Liberty, and the Pursuit of Happiness (which was property) Consent of the Governed Genocidal Policy of killing or extinguishing a group (based on religion, ethnicity, race, etc) "City on a Hill" John Winthrop (Puritan governor) described Massachusetts Bay Colony Indentured Servants Sign contract to work for 4-7 years in exchange for passage to the New World The number of Indentured Servants decreases after Bacon's Rebellion Mostly in Southern colonies Types of Colonies