Employment Law
advertisement

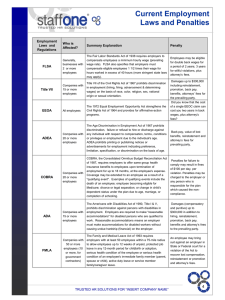
Employment Law Employment – at – will 1 Employment-at-will is not a law; it is a doctrine based on common law. Either the employee or the employer may terminate the employment relationship at any time and for any reason – a good reason, a bad reason or no reason at all. There are exceptions. Age Discrimination in Employment Prohibits discrimination in employment for persons age 40 and Act of 1967 (ADEA) over except where age is a bona fide occupational qualification Americans with Disabilities Act of Prohibits discrimination against a qualified individual with a 1990 (ADA) disability because of the disability of such individual; protects 2009 ADAAA qualified individuals with disabilities from unlawful discrimination in the workplace, including access to training and career development. ADAAA expanded the definition of disability and the two non-exhaustive lists of “major life activities”. Rehabilitation Act of 1973 Prohibits discrimination based on physical or mental disabilities; requires employers to make reasonable accommodation for the physical or mental disability unless there is undue hardship; applies only to the federal government or federal contractors with contracts over $10,000. Consumer Credit Protection Act Protects employees from discharge by their employers because (CCPA) their wages have been garnished for any one debt, and it limits the amount of an employee's earnings that may be garnished in any one week. Employee Polygraph Protection Act Prohibits most private employers from using polygraph tests, either (EPPA) for preemployment screening or during the course of employment. Title VII of Civil Rights Act (1964) Title VII prohibits discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin. Civil Rights Act of 1991 In cases of intentional employment discrimination, allows for monetary damages. Equal Pay Act of 1963 (EPA) Protects men and women who perform substantially equal work in the same establishment from sex-based wage discrimination. Fair Credit Reporting Act Promotes the accuracy, fairness, and privacy of information in the files of consumer reporting agencies. Applies to employers who order consumer reports from a consumer reporting agency (third party background checks). Applicant must be notified, in writing, of intent to obtain report and we must get their written permission before requesting one. Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) Establishes minimum wage, overtime, and record keeping standards for employees who are not exempt from its provisions. Also covers child labor. In 2010 added requirement for nonexempt nursing mothers; private room with breaks to accommodate nursing or expressing milk for infant. Family Medical Leave Act (FMLA) Provides an entitlement of up to 12 weeks of job-protected, unpaid leave during any 12-month period. National Defense Authorization Act Provides additional FMLA leave for military families. Specifically, the bill adds two new FMLA-qualifying events, expanding FMLA to include employees caring for an injured service member (26 weeks of leave) as well as family members who have a family member called to active duty. Employment Law GINA – Title II 2009 Immigration Reform and Control Act (IRCA) of 1986 Lilly Ledbetter Fair Pay Act 2009 Pregnancy Discrimination Act of 1978 (PDA) Uniformed Services Employment and Reemployment Rights Act of 1991 (USERRA) Worker Adjustment and Retraining Notification Act (WARN) 2 Title II prohibits discrimination against employees or applicants because of genetic information; prohibits the use of genetic information in making employment decisions, restricts acquisition of genetic information by employers and other entities covered by Title II, and strictly limits the disclosure of genetic information. Requires completion of the I9 (Employment Eligibility Verification Form) to verify that every employee hired after 11/06/1986 is authorized to be employed in the United States. Reset the statute of limitations to occur each time an employee receives a paycheck. Protects pregnant women from employment discrimination and requires employers to be non-discriminatory in providing employee benefits such as: Health insurance, sick leave, pensions, and vacation time. The pre-service employer must reemploy service members returning from a period of service in the uniformed services if those service members meet five criteria. Requires some employers to give a minimum of 60 day’s notice if a plant is to close or if mass layoffs will occur