Reducing the Risks of
Employment Lawsuits
Laws …. Laws …. Laws ….
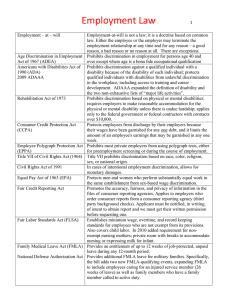
Federal Civil Rights
Federal Wage and Hour
Federal Employment
State Employment
Federal
Civil Rights
Laws
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964
Prohibits discrimination in
employment based on race, sex,
color, religion, or national origin.
Two types of discrimination cases:
1. Disparate Treatment Cases
2. Disparate Impact Cases
Age
Discrimination in Employment Act
Prohibits discrimination in employment
based on age
Protected class consists of people 40
years and older
Pregnancy
Discrimination Act of 1978
Employers cannot discriminate in employment
based on pregnancy related conditions
Cannot refuse to hire applicants because they
are pregnant
Cannot fire employees because they become
pregnant
Employers must treat pregnancy as any other
illness or disability
Same reemployment rights as other
employees that go on leaves of absence for
other disabilities or illnesses
FMLA
Family and Medical Leave Act
Employers are required to provide
eligible employees with up to 12
weeks of unpaid leave per year for:
birth, adoption or placement of a child or
care for the same
“serious health condition” for spouse,
parents or children.
FMLA
Covered employee
12 month period
Can take PTO and EDL during
Must complete form to request
Tracking “absences”
Define “serious health condition”
Americans with Disabilities Act
Employers may not discriminate against a
qualified individual with a disability in
recruitment, advertising, job applicant
procedures, hiring, upgrading, promoting,
seniority, demotion, transfer, layoff,
termination, return from layoff, rehiring, pay,
job assignments, leaves of absence, sick
leave, selection for training, etc.
ADA
Who is considered disabled?
What does the law provide?
Employer may not discriminate
Employers must make reasonable
accommodations as long as it
does not cause an undue hardship
What you can/cannot ask
Federal
Wage & Hour
Laws
Fair Labor Standards Act
Minimum Wage Provisions
Overtime Provisions
Exceptions – “Exempt” Employees
Executive
Administrative
Learned Professional
Creative Professional
Computer Professional
Outside Sales
Highly Compensated Employee
Equal Pay Act
Prohibits paying lower wages to
employees of one sex than are paid to
employees of another sex for “equal work”
Four factors taken into consideration:
1. Skill
2. Effort
3. Responsibility
4. Similar working conditions
Common Wage & Hour FAQs
Can employees be required to work
overtime?
Can you require lunch/rest breaks?
Does the law require them?
How should time cards be handled?
Common overtime mistakes:
Allowing non-exempt employees to begin or end
work before or after their assigned hours
Allowing non-exempt employees to work through
their lunch breaks
Allowing non-exempt employees to take work
home
Counting PTO as work time
Docking salaried exempt employees for partial
day absences
Employee or Independent
Contractor?
Factors to consider:
Behavioral control
Financial control
Definition of Relationship
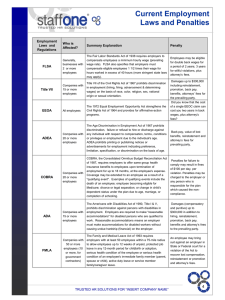
Other Federal Employment Laws
Immigration Reform and Control Act
Fair Credit Reporting Act
FACTA
USERRA
Jury System Improvement Act
National Labor Relations Act
Polygraph Protection Act
WARN
Drug Free Workplace Act of 1989
COBRA
HIPAA
CRITICAL Legal Issues Facing
Management
Employment-At-Will
Wrongful Discharge
Harassment
Document
Document Document
Document Document
Recruiting and Hiring
The Hiring Process
Legally Recruiting Quality Candidates
Legal Problems in Interviewing
Rejecting Unsuitable Applicants
Reference Checking
Pre-Employment Testing
Document
Document
Document Document
Document Document
Managing Employees Legally
Establishing Job Standards
Job Descriptions
Job Assignments and the Law
Dealing with Performance Problems
Document
Document
Document Document
Document
Performance Reviews
When performance reviews cause
legal problems
How to reduce vulnerability
Biggest DANGER – not being honest
with the employee
Document
Document
Document Document
Document
Dress Codes
What we can require/prohibit
What can cause problems
Regarding Employee…
…Right to Privacy
…Searches
…Telephone Calls
…Cell-phone Policies
…E-mail
…Internet use
Disciplinary Procedures and the Law
Two conditions necessary to be effective:
Tell them WHAT you expect
Tell them WHY you expect it
Discipline Procedure
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Friendly Warning
Verbal Warning
1st Written Warning
2nd Written Warning (if applicable)
Termination (if applicable)
Document
Document
Document Document
Document
Legally Terminating Employees
Resignation or discharge?
The truth about firing:
– Firing poor performers raises morale
– Don’t feel bad
Checklist For Lawful Terminations
Was there a written rule or regulation?
Was the employee informed of it?
Was the rule administered fairly and
consistently?
Do you have adequate written
documentation?
Have you thoroughly investigated the facts?
Has the employee been presented with an
opportunity to present their side of the story?
Ask Yourself
Is it fair?
Would it seem fair to a judge?
Unemployment Claims
What is the impact on the agency?
Who is eligible?
What is the process?
If you have done it right, you are
now VERY happy!
Questions?
Mary A. Flores
VP of HR for BBBSNT
Wk. 817.277.1148 ext. 242
Cell 214.288.3678
mflores@bbbsnt.org