Primates:
advertisement

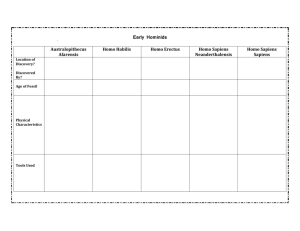
Primates: Binocular Hands Human Ancestors? Fossil Evidence claws) Monkeys: (tails) no tails Hominids (bipedalism, slower, but able to use hands for purposes other than ambulation). Apes: Pangea Primitive Primates 70 Small Super continent 200 m BP Plate tectonics caused super continent to break apart. Change in land mass location led to climate change. Global cooling also led to shrinking of forests which permitted the emergence of grasslands. – 30 m BP eyesight: depth perception that can grasp (nails not m BP (Montana) the size of squirrels, tree shrews. Arboreal (tree dwelling) The forest savannah fringe was a new unexploited habitat, the emancipation from the trees favored a larger body size. – Larger primates are no longer arboreal Limitations of Physical Anthropology Tree Shrew New fossil discoveries lead to revisions of previous facts! Unclear where to look for fossils, and when they y will be found. Unclear when you should stop looking at one site and begin to explore another one. The rules to document ancestry are unclear. 1 Lumpers vs. splitters It is unclear how much range of variation occurs within a species. No two “experts” evaluate the available y data the same way. Lumpers: individuals who see differences as variation within the same species. Splitters: individuals who perceive the differences as evidence for a new species. Debates Scientist challenges interpretation of new find, the oldest primate fossil ever discovered Find opens debate about whether man's earliest ancestors came from Asia and were diurnal or nocturnal Debates "It was once thought that primates originated in North America because that's where the earliest fossils were found initially; but we should be more open open--minded. We still do not know the area of origin of the primate lineage that eventually led to humans, and this new find firmly brings Asia into the picture." Current Thinking Several species of early hominids may be living at the same time. Debates "I disagree with the authors on both statistical and biological grounds!" Time Line: Note that as many as 4-5 species of early hominids were living at the same time. A parental species may continue to exist after a daughter species evolved. A parental species may continue to exist after a daughter species emerges. 2 Current Thinking Bipedalism brain size Bipedalism precedes increments in brain size precedes increments in Aegyptopithecus Aegyptopithecus 28 28--30 m BP Tail Tail--less Africa/Asia Ancestral to all apes and hominids – Gave rise to three genera (12 m BP): Gigantopithecus Dryopithecus Ramapithecus Keel Dimorphism Sagital keel differences The large keel is evidence of large strong muscle insertion. Is the dimorphism evidence of sexual dimorphism, dimorphism or two different species? 3 Gigantopithecus Gigantopithecus Asia – wide spread Size of modern gorilla Extinct @ 1 m BP Dryopithecus Dryopithecus Woodland Ancestor ape to all modern apes Ramapithecus Ramapithecus Africa, Asia, Europe Up right posture Forest/savannah fringe Seed eater: good molars molars, small canine teeth 3 ½’ tall No evidence of tool use Rather small brain 4 Fossils Density Poor between 12 m BP and 3 m BP. Australopithecus afarensis 3 m BP to present much richer fossil d density. it Australopithecus afarensis Australopithecus africanus 3 ½ m BP Australopithecus africanus Australopithecus boisei 3 m BP tall 60# 600 cc 4’ 5 Australopithecus boisei Homo erectus 2 ¼ m BP 5’ tall 150# 600 + cc Homo erectus 1 m BP ‘ tall 700 to 1,300 cc (modern humans 1 300 cc) 1,300 Reduction in sexual dimorphism H. erectus was once believed to be ancestral to modern humans. Currently some authorities believe that it is not ancestral to humans. 5 Oldest tools @ 2.6 m BP Homo sp?? Unclear when the 1st members of the Homo genus emerged. 2 ½ m BP is a common estimate. Stone tools emerged 22-3 m BP. Oldest tools @ 2.6 m BP About 2,600 tools in this age bracket have been found in Ethopia. 6 Tool Industries Oldowan tools (choppers) Oldowan – Primative choppers and scrapers Acheulean h l – Well formed hand axes Acheulean flake tools (Zambia, 200,000-400,000 ybp) Oldowan tools (flake) Tool Industries Both the Oldowan and Ascheulean tools are found at the same sites and the same period in time. Were they made by separate species??? Acheulean scrapper (left) from Zambia, late stone age scrapper (right) from Texas. These tools were made 200,000 years apart in time. 7 The tool on the right.. Homo sapiens (archaic) Was made in Texas by a fully modern human after Columbus discovered the New World. H. Sapiens 17,000 BP Homo sapiens Modern people emerged 200,000 to @ 90,000 BP. Extended use of fire Burial B i l off dead d d Cave art Language? Homo sapiens neanderthalensis Homo sapiens neanderthalensis 200,000 – 35,000 BP. Use of fire Burial of dead Cave art? Language?? Brain @ 1600 cc (larger than modern humans?) Heavy brow ridge – primitive trait? Extinct line of humans, or natural variation?? 8 Cave Art? Oldest Cave Paintings @ 35,000 BP If Neanderthal man created any form of art, no traces of it have yet been found. These are probably the oldest cave paintings, although we cannot affirm that with scientific certainty. The cave contains traces of Neanderthal man and evidence of habitation by modern Homo sapiens. "The traces we have found show a clean break between Neanderthal and modern man both in terms of culture and lifestyle. There is an abrupt change in the techniques of decoration and the use of flint and bone tools. Everything changes, in a radical, brutal fashion." fashion." "It's not impossible that the Chauvet cave was painted by Neanderthals.” Neanderthal Art? Homo Brain Volume Neanderthal Flute?? Time Line: Note that as many as 4-5 species of early hominids were living at the same time. A parental species may continue to exist after a daughter species evolved. 9 Earliest Use of Fire?? Archaeologists in Israel may have unearthed the oldest evidence of fire use by our ancestors. The site, site on the banks of the Jordan River, dates to about 790,000 years ago. There are older sites in Africa, but the evidence from these is much more hotly contested. Fire The team analyzed over 50,000 pieces of wood and nearly 36,000 pieces of flint from what was once probably a Homo erectus settlement on the shores of an ancient lake. Flint was examined because it was used for tool making and shows a characteristic pitting when exposed to fire. Fire The oldest evidence of fire use in Europe dates from around 500,000 BP. Early y use of fire precedes p modern Homo sapiens by about 500,000 years. Fire may have been used by hominids not ancestral to modern humans. Hobbit--Like Human Ancestor Hobbit Found in Asia Homo sapiens (modern) Note: the primitive trait of the retention of facial fur Flores Scientists have found skeletons of a hobbit-like species of human that hobbitgrew no larger than a threethree-year year--old modern child child. The tiny humans, humans who had skulls about the size of grapefruits, lived with pygmy elephants and Komodo dragons on a remote island in Indonesia 18,000 years ago. 10 Hobbit--like Human Hobbit Relative size: pygmy, European, flores Recent Discoveries Flores skull compared to modern humans Homo floresiensis Flores tools Brain volume: 380 cc in the lower range for chimps, and primitive Australopithecines. 3 ½ ‘ tall 55 # Stone tools 11 Flores Became extinct about 18,000 BP. This is about 12,000 after humans crossed into North and South America. America A totally unexpected discovery. Oldest Pottery China: Oldest Writing? Egypt – 5,500 BP 16,000 – 13,000 BP Oldest Alphabet?? Late Bronze Age – 3,500 BP Modern Times @ 16,000 BP @ 12,000 BP Agriculture @ 10,000 BP Tool Ages Pottery Stone Domestication Copper @ 3 m BP @ 6,000 BP Bronze @ 5,500 BP Iron @ 3,000 BP Writing: pictographic @ 5,500 BP Writing: phonetic @ 3,500 BP 12