Prehistory Study Guide for Unit Test
advertisement

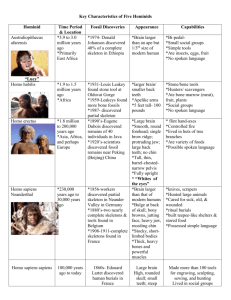
Prehistory Study Guide for Unit Test This is a place to start studying. You should also review the textbook (section 4 and 5 of chapter one and all of chapter two), notes and all worksheets. Prehistory – period of time before recorded history Fossils – imprint of a dead thing Artifacts – things made by man Remains – actual parts of a dead thing ( bones, teeth ) Anthropology – study of characteristics of customs of people cultural – how people live physical – how people look Archaeology – study of the past through excavation Philosophy – study of life, truth, reality, and things with no answers Legends – stories passed through generations that explain something Excavate - digging Carbon 14 dating – a way archaeologists can tell the age of Specimens that were once alive Willard Libby – discovered how to use carbon dating 14 Mary Leaky – discovered prehuman footprints 3.6 million years old Charles Darwin – created the idea of the “survival of the fittest” Natural selection – only the strongest of the species survives Paleolithic Age – Old Stone Age Band – group of 30-50 people Specialization – development of jobs Lucy – Australopithecus Africanus – one of the earliest prehumans discovered Neanderthal – first humans to bury their dead, named after the Neander River in Germany Homo habilis – “ Man with ability” Homo erectus – “ Man who walks upright” Homo sapiens – “Man who thinks” Australopithecus – southern ape Ramapithecus – tooth pattern is like man Pitfalls – used to capture animals Cro-Magnon – first to practice art Burin – tool that looks like a chisel Spear throwers – weapon used to capture animals Chief – Neolithic ruler (government) Land bridges – how early humans were able to leave Africa Shaman - priest