Discussion 10: Signaling MCB 150
advertisement
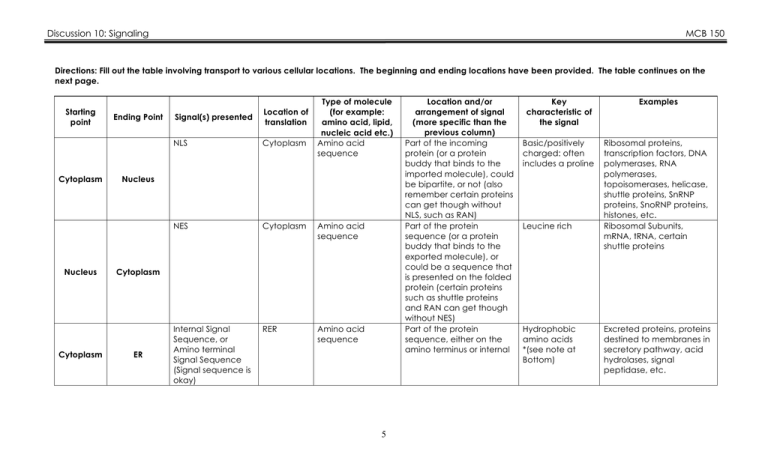
Discussion 10: Signaling MCB 150 Directions: Fill out the table involving transport to various cellular locations. The beginning and ending locations have been provided. The table continues on the next page. Starting point Cytoplasm Nucleus Cytoplasm Ending Point Type of molecule (for example: amino acid, lipid, nucleic acid etc.) Amino acid sequence Signal(s) presented Location of translation NLS Cytoplasm NES Cytoplasm Amino acid sequence Internal Signal Sequence, or Amino terminal Signal Sequence (Signal sequence is okay) RER Amino acid sequence Nucleus Cytoplasm ER 5 Location and/or arrangement of signal (more specific than the previous column) Part of the incoming protein (or a protein buddy that binds to the imported molecule), could be bipartite, or not (also remember certain proteins can get though without NLS, such as RAN) Part of the protein sequence (or a protein buddy that binds to the exported molecule), or could be a sequence that is presented on the folded protein (certain proteins such as shuttle proteins and RAN can get though without NES) Part of the protein sequence, either on the amino terminus or internal Key characteristic of the signal Basic/positively charged: often includes a proline Leucine rich Hydrophobic amino acids *(see note at Bottom) Examples Ribosomal proteins, transcription factors, DNA polymerases, RNA polymerases, topoisomerases, helicase, shuttle proteins, SnRNP proteins, SnoRNP proteins, histones, etc. Ribosomal Subunits, mRNA, tRNA, certain shuttle proteins Excreted proteins, proteins destined to membranes in secretory pathway, acid hydrolases, signal peptidase, etc. Discussion 10: Signaling RER Golgi Cytoplasm Golgi Lysosome MCB 150 11 mer (would have to have a signal sequence first, then the 14 mer which gets modified to the 11 mer) mannose-6phosphate RER Carbohydrate or oligosaccharide Starts out on dolichol, gets transferred via N linked glycosylation onto an asparagine molecule of the incoming protein Branched chain of sugars arranged in a particular manner proteins that function in the golgi, acid hydrolase, anything that is going through secretory pathway RER Mannose-6phosphate 6th mannose of the 11 mer See the previous 2 answers acid hydrolases mitochondrial transit sequence (or presequence) Cytoplasm Amino acid sequence Part of the transported protein at the amino terminus Basic/positively charged amino acids Mt ribosomal proteins, mt DNA and RNA polymerases, transit peptidase (MPP), chaperone proteins, chaperonin proteins, anything needed for ETC not present in mt genome, porins, etc. Mitochondria 6







