Immunology Phagocytes Killer T-cells Macrophages
advertisement

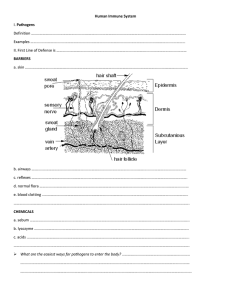
Phagocytes Killer T-cells Immunology Macrophages Natural Killer Cells Immune System Group of cells in the body that recognize foreign substances F(x) = to neutralize or destroy all things “non-self” (pathogens or invaders) What is a Pathogen? Any toxin, living organism, or other agent that can cause disease. Immune Cells Immune cells circulate throughout the body in the blood system and the lymphatic system Lymphatic System A network of vessels that penetrate nearly every tissue of the body, and a collection of tissues & organs that produce immune cells F(x): Fluid recovery from tissues Lymph = fluid Immunity Lymph is filtered before returning to blood Lymph Tissues & Organs Lymph Nodes Clean the lymph & alert the immune system to pathogens Tonsils Guard against ingested or inhaled pathogens Thymus Produces T-cells Spleen (largest Lymph Organ) Monitors blood for foreign objects Recycles old RBCs TONSIL Body Defense - Two Types 1. Non-Specific 2. Specific Non-Specific Body Defense Innate or inborn, not affected by prior exposures NOT specific for any invader Operates constantly Non-Specific Body Defense SKIN – 1st Line of Defense Physical barrier = prevents entry of pathogens Must be unbroken to be effective Acidic, oily, sweat glands– inhibits bacterial growth Non-Specific Body Defense MUCUS MEMBRANES Respiratory, Digestive, Urinary, Reproduction tracts F(x): To trap debris & pathogens Non-Specific Body Defense HAIRS Nasal passage Traps debris & pathogens CILIA Upper Respiratory Tract Traps debris & pathogens Non-Specific Body Defense CELLULAR Activated DEFENSE when other defenses are breached Two Types: Phagocytes Leukocytes Phagocyte eating dying cells. Phagocytes Cell’s F(x): that recognize “non-self” items engulf or “eat” foreign debris Reside in lymph organs Travel to the site of infection, via the blood stream Macrophage – a type of phagocyte Leukocytes (Natural Killer Cells) a.k.a. NK Cells WBCs police the blood & lymph F(x): Bind to membrane of the invader, release chemicals, cause infected cell to lyse Non-Specific Body Defense CELLULAR (TISSUE) DEFENSE Inflammatory Fever Response Inflammation Local defensive response to tissue injury of any kind Response Helps is directly at site of injury to prevent spread of the damaging agent Inflammation The 4 Signs of Inflammation – S.H.A.R.P. Swelling Heat ↑ All four of these – due to fluid build-up ↓ Redness Pain Fever Abnormal elevation in body temp. Response Stimulates Heat to infection phagocytes to go to work kills many pathogens Increases the rate of enzymatic rxns Non-Specific Body Defense CHEMICAL Interferons DEFENSE (antiviral proteins) Interferons Secreted by virus-infected cell Stimulates non-infected cells to make proteins that block viral protein synthesis Slows infection to allow specific defenses to begin working Activates macrophages to “eat” (non-self) viral invaders Specific Body Defense Immunity = ability to ward off a specific infection or disease Highly specific resistance to disease Process: Particular invader recognized Switches on immune response Invader is remembered so that future invasions can be immediately fought Specific Body Defense Specific Body Defense is born out of the Lymphatic System Bone marrow makes B-cells, which make specific antibodies i.e. Antigens Irritant or pathogen– molecule that react with antibodies Epitope = region of antigen recognized by a specific antibody Stimulates formation of antibodies Antibodies Molecules that react with or bind to antigens Mark antigens for destruction by macrophages Form due to the exposure to a specific antigen Antibodies Made by B-cells Found Once in plasma, & all body secretions present, allows immediate immune response to pathogens Antibodies Structure (most common) Composed of 2 heavy chains, 2 light chains Constant & Variable regions Antigen-binding site Variable region Constant region Specific Body Defense Helper T-cells Attract other T-cells (Killer T-cells) and macrophages to an antigen Killer T-cells Directly attack & kill pathogens, release chemicals to lyse cells Specific Body Defense Suppressor T-cells Stops immune response when antigen is successfully overcome Scanning Electron Micrograph of a T-cell Specific & Non-specific Defenses work together to protect the body from disease-producing pathogens B-cells mature in bone tissue T-cells mature in thymus tissue Applications of Immune Response Immunization= process that increases an organism’s rxn to antigen & therefore improves its ability to resist or overcome infection. Vaccine= living or inactivated organism used to induce specific immunity Vaccines Attenuated agents: Virus/bacteria that has been modified to be incapable of causing disease Inactivated Pieces agents: or a whole organism that has been chemically inactivated Can’t reproduce but retains antigenicity Immunity 3 Types: Active Passive Cell Mediated Active Immunity When an individual responds to an antigen Resulting from vaccination against or Recovery from a natural infection Permanent Immunity Passive Immunity Antibodies produced from another organism injected into the body Temporary protection against disease Cell-Mediated Immunity Killer T-cells attack any cell not marked with a special protein (i.e. cells that are “non-self”)