Thermodynamics: Temperature, Thermal Equilibrium & Expansion
advertisement

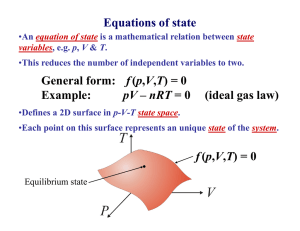
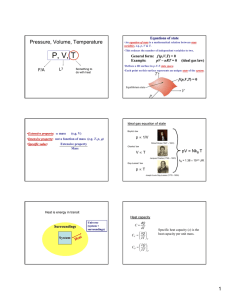
Thermodynamics I. Temperature 1. Thermal equilibrium. Zeroth law of thermodynamics a) We need a thermometer b) Thermal equilibrium c) Zeroth law: If C is in thermal equilibrium with both A and B, then A and B are also in thermal equilibrium with each other d) Temperature Two systems are in thermal equilibrium if and only if they have the same temperature 2. Temperature scales TC: 0°C - freezing of water, TF = (9/5) TC+32 Tk = TC +273.15 100°C - boiling of water TC = (5/9) (TF - 32) The temperature of an ideal monatomic gas is a measure related to the average kinetic energy of its atoms as they move. In this animation, the size of helium atoms relative to their spacing is shown to scale under 1950 atmospheres of pressure. These room-temperature atoms have a certain, average speed (slowed down here two trillion fold). Heating a body, such as a segment of protein alpha helix, tends to cause its atoms to vibrate more, and to cause it to expand or change phase. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Temperature Question Two thermometers are in thermal equilibrium with each other. One reads in ˚C and one reads in ˚F. At what temperature do they read the same number? That is, at what temperature is T(˚C) = T(˚F)? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 40 20 0 -20 -40 2a. The absolute (Kelvin) scale and gas thermometer The Gay-Lussaec law For an ideal gas at V=const: P1/T1= P2/T2 P T(°C) -273.15°C P/T=const 0°C P V1 V2 > V1 P 0 273.15 T(K) Definition: Ttriple = 273.16 K = 0.01 ºC T(K) P P T Ttriple 273.16 Ptriple Ptriple 3. Thermal expansion T0, L0 T = T0 + ΔT, ΔL = α L0ΔT L = L0 + ΔL L - L0 = α L0ΔT L = L0 (1 + α ΔT) ΔV = β V0ΔT V = V0 (1 + β ΔT) β = 3α V=L3 L V = L3 =[L0 (1 + α ΔT)]3 = L0 3 (1 + α ΔT) 3 ~ ~ L0 3 (1 + 3α ΔT) ΔA = 2 α A0ΔT A= A0 (1 + 2 α ΔT) L L A=L2 L Example 1: An aluminum flagpole is 33m high. By how mach does its length increase as the temperature increases by 15 °C? L0 = 33 m ΔT = 15°C α = 25x10-6 (C ° )-1 ΔL - ? ΔL = α L0ΔT ΔL = [25x10-6 (C ° )-1]x (33 m) x (15°C) =1.2x10-2 m Example 2: A donut shaped piece of metal is cooled and its temperature decreases. What happened with inner and outer radii after cooling? Both radii decrease! Question A steel measuring tape is 10.000 m long at 20 ˚C. The increase in length of the measuring tape upon heating to 40 ˚C is ___ mm. (For steel, = 1.2 x 105/˚C) 1. 2. 3. 4. 0.8 1.6 2.4 3.2