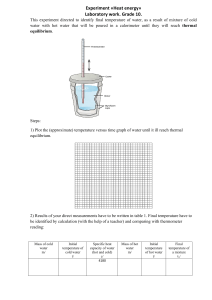
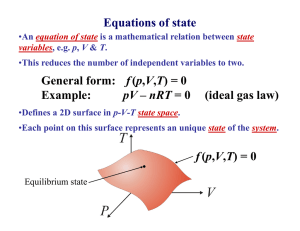
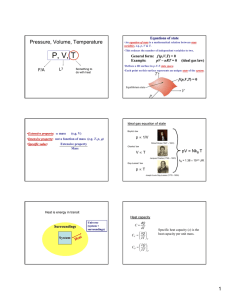
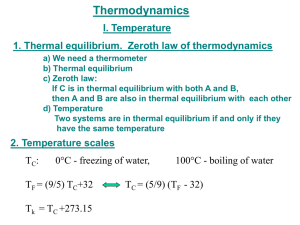
CHAPTER 4 Temperature, Heat & Thermal Equilibrium THINK IT OVER HEAT = TEMPERATURE? MORE HEAT = MORE TEMPERATURE? Heat - energy transfers from one object to another because of temperature difference Temperature - measure of the average kinetic energy of the atoms and molecules in substance BRAIN POWER Temperature Heat Definition Measure of the A form of energy degree of hotness Characteristic Determines the direction of heat flow Transfer of energy from a region of higher temp. to another region of lower temp. Classification Base quantity Derived quantity SI Unit Kelvin, K Joule, J Other unit Celsius, oC Calorie, cal Learning Outcomes At the end of the lesson, students should be able to: 1) explain thermal equilibrium 2) explain how a liquid-in-glass thermometer works. How Does Thermal Equilibrium Achieve? Mechanism of Thermal Equilibrium A HOT Faster rate of energy transfer from HOT to COLD + B COLD Slower rate of energy transfer from COLD to HOT HOT COLD HOT COLD Energy transferred at the same rate between HOT and COLD A B No NET HEAT transfered THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM : 1 2 Two object have same temperature No net flow of heat between two objects Liquid-in-glass thermometer Mercury Freezing point : -39oC Boiling point : 357oC Alcohol Freezing point : -115oC Boiling point : 78oC It does not wet the tube Opaque. Easy to read. Poisonous Expensive Conduct heat well, responds faster to temperature changes. It wet the tube. Colorless. It needs to be dyed. Safe liquid Cheap Responds more slowly than mercury. Liquid-in-glass thermometer Calibration ( Penentukuran ) Mercury is used because : Opaque (Legap) - easy to take reading Expands ( mengembang) uniformly with heat - uniform scale High cohesive force ( daya lekitan tinggi ) - not stick to glass wall High Boiling point - measure high temperature Improve sensitivity 1. Narrow capillary tube 2. Thin glass wall bulb (bebuli) 3. Small bulb ( bebuli) HOMEWORK Read about specific heat capacity and write your own notes. Ready for class after school break. SELAMAT BerPHYSICS Bye2