Basic Biology Related to Technology for Measuring Gene Expression
advertisement
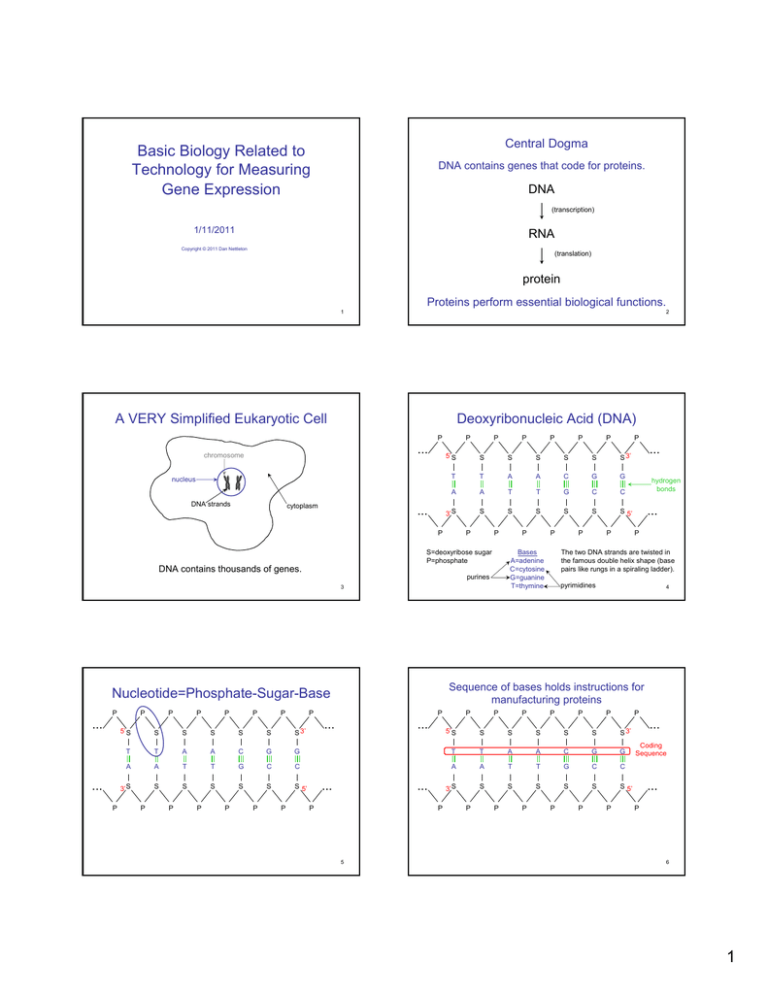
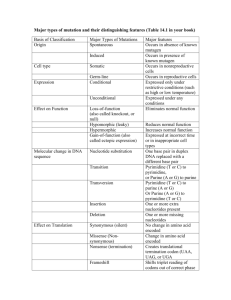
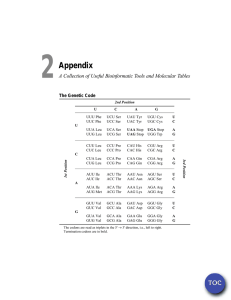
Central Dogma Basic Biology Related to Technology for Measuring Gene Expression DNA contains genes that code for proteins. DNA (transcription) 1/11/2011 RNA Copyright © 2011 Dan Nettleton (translation) protein Proteins perform essential biological functions. 1 2 A VERY Simplified Eukaryotic Cell Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) P ... chromosome nucleus DNA strands cytoplasm ... P P S S S 3’ T T A A C G G A A T T G C C 3’ S S S S S S S 5’ P P ... P P P P 5’ S S S S S S S 3’ T T A A C G A A T T G 3’ S S S S S P P P P P P P P hydrogen bonds ... P The two DNA strands are twisted in the famous double helix shape (base pairs like rungs in a spiraling ladder). pyrimidines 4 P ... ... P P P P P P P 5’ S S S S S S S 3’ G T T A A C G G C C A A T T G C C S S 5’ 3’ S S S S S S S 5’ P ... Sequence of bases holds instructions for manufacturing proteins Nucleotide=Phosphate-Sugar-Base P P Bases A=adenine C=cytosine G=guanine T=thymine purines P P S 3 P P S DNA contains thousands of genes. P P S S=deoxyribose sugar P=phosphate P P 5’ S P ... P ... ... P P 5 P P P P P P ... Coding Sequence ... P 6 1 RNA Polymerase Transcription • An enzyme is a protein that catalyzes chemical reactions. P ... • RNA polymerase is the enzyme responsible for transcribing DNA to RNA. ... P P P P P P P 5’ S S S S S S S 3’ T T A A C G G A A T T G C C 3’ S S S S S S S 5’ P P P P P P P ... ... P 7 8 Transcription P ... ... P P P P Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) P P P 5’ S S S S S S S 3’ U U A A C G G A A T T G C C 3’ S S S S S S S 5’ P P P P P P P P ... ... ... P P P P P 5’ S S S S S S S 3’ U U A A C G G S=ribose sugar P=phosphate P P P Bases A=adenine C=cytosine G=guanine U=uracil ... The product of transcription is known as the primary transcript. 9 Posttranscriptional Modifications to Primary Transcript 10 Expression Levels Primary transcript 5’ UTR 3’ UTR Intervening sequences corresponding to introns that are removed through splicing Primary transcript after modification: messenger RNA (mRNA) G 5’ cap 5’ UTR 3’ UTR Coding portions of RNA sequence corresponding to exons AAAAAA...AAAA • The amount of messenger RNA (mRNA) produced by a gene is known as the gene's expression level. • This course focuses on the design and analysis of experiments that involve the simultaneous measurement of gene expression levels for thousands of genes. poly-A tail 11 12 2 Translation Transcription takes place inside the nucleus. Ribosome chromosome mRNA nucleus DNA strands cytoplasm amino acid sequence folds to become a protein Translation takes place outside the nucleus. 13 During translation transfer RNA (tRNA) translates the genetic code ... U A U A U A U C G G C tRNA anticodon leu U C G A U UUU UUC UUA UUG phe phe leu leu UCU UCC UCA UCG ser ser ser ser UAU UAC UAA UAG tyr tyr STOP STOP UGU UGC UGA UGG cys cys STOP trp C CUU CUC CUA CUG leu leu leu leu CCU CCC CCA CCG pro pro pro pro CAU CAC CAA CAG his his gln gln CGU CGC CGA CGG arg arg arg arg A AUU AUC AUA AUG ile ile ile met ACU ACC ACA ACG thr thr thr thr AAU AAC AAA AAG asn asn lys lys AGU AGC AGA AGG ser ser arg arg G GUU GUC GUA GUG val val val val GCU GCC GCA GCG ala ala ala ala GAU GAC GAA GAG asp asp glu glu GGU GGC GGA GGG gly gly gly gly ... G amino acid Second Base codon A mRNA codon The Genetic Code First Base codon 14 thr amino acids 15 16 Miscellaneous Comments • The biology is more complicated than I described. • It is amazing! • Humans have somewhere around 30,000 genes. (The exact number is a subject for debate.) • Much of the variation is created by differences in how cells use the genes they have. • Microarrays and Next Generation Sequencing are tools that can help us understand how cells of various types use their genes in response to varying conditions. This helps us to understand gene function. 17 3