Types of mutations chart
advertisement

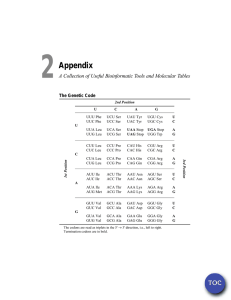
Major types of mutation and their distinguishing features (Table 14.1 in your book) Basis of Classification Origin Major Types of Mutations Spontaneous Induced Cell type Somatic Expression Germ-line Conditional Unconditional Effect on Function Molecular change in DNA sequence Loss-of-function (also called knockout, or null) Hypomorphic (leaky) Hypermorphic Gain-of-function (also called ectopic expression) Nucleotide substitution Transition Transversion Insertion Deletion Effect on Translation Synonymous (silent) Missense (Nonsynonymous) Nonsense (termination) Frameshift Major features Occurs in absence of known mutagen Occurs in presence of known mutagen Occurs in nonreproductive cells Occurs in reproductive cells Expressed only under restrictive conditions (such as high or low temperature) Expressed under any conditions Eliminates normal function Reduces normal function Increases normal function Expressed at incorrect time or in inappropriate cell types One base pair in duplex DNA replaced with a different base pair Pyrimidine (T or C) to pyrimidine, or Purine (A or G) to purine Pyrimidine (T or C) to purine (A or G) Or Purine (A or G) to pyrimidine (T or C) One or more extra nucleotides present One or more missing nucleotides No change in amino acid encoded Change in amino acid encoded Creates translational termination codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA Shifts triplet reading of codons out of correct phase The Genetic Code (DNA) TTT Phe TCT Ser TAT Tyr TGT Cys TTC Phe TCC Ser TAC Tyr TGC Cys TTA Leu TCA Ser TAA STOP TGA STOP TTG Leu TCG Ser TAG STOP TGG Trp CTT Leu CCT Pro CAT His CGT Arg CTC Leu CCC Pro CAC His CGC Arg CTA Leu CCA Pro CAA Gln CGA Arg CTG Leu CCG Pro CAG Gln CGG Arg ATT Ile ACT Thr AAT Asn AGT Ser ATC Ile ACC Thr AAC Asn AGC Ser ATA Ile ACA Thr AAA Lys AGA Arg ATG Met* ACG Thr AAG Lys AGG Arg GTT Val GCT Ala GAT Asp GGT Gly GTC Val GCC Ala GAC Asp GGC Gly GTA Val GCA Ala GAA Glu GGA Gly GTG Val GCG Ala GAG Glu GGG Gly *When within gene; at beginning of gene, ATG signals start of translation.