DNA Similarities
advertisement

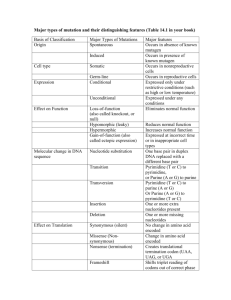
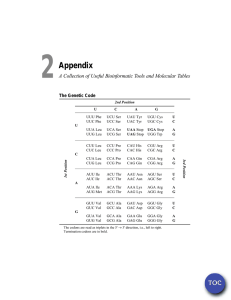
DNA Similarities Suppose you could compare the total DNA sequences of various organisms (some billions of base pairs). How much similarity would you expect between a whale and a fish? A whale and a dog? A dog and a shrimp? A shrimp and a bacterium? As always, there are two types of similarity to be considered: analogy and homology. If the sequences show similarity because they code for proteins with similar functions, analogy would be the explanation. If the sequences show similarity because of common ancestry, then it is homology. We now have techniques for determining DNA sequences rapidly, and we know the sequences of the entire genome for many organisms. The entire human genome was finished in 2003. Surprisingly, only a small portion of the DNA of higher plants and animals is actually genes. Some of the rest is involved in controlling when genes are transcribed; but a lot of the DNA seems to be just "filler," or "junk DNA." Experiments in which changes are made in these regions show no effect on gene function at all. For most higher plants and animals, the amount of DNA which actually codes for proteins is 5% or less. Even allowing for control sequences, at least 90% of the DNA is functionless, and rather variable even within species. Suppose there is a species of mice, and a small population becomes isolated. Reproductive isolation occurs, and there are now two species of mice. I know you are not a molecular biologist. Just speculate. 1: How could the sequences of their filler DNA change? 2: Does every mutation that changes the DNA sequence within a gene cause a change in protein function? Refer to the attached genetic code table. Notice that different codons often specify the same amino acid. Of the three nucleotides of a codon, first, second, and third, which one may be changed most often without changing the amino acid coded for? 3: Suppose you have two species which have originated from a common ancestor. You compare their DNA sequences. What factors would influence the amount of difference between the sequences? FIRST LETTER U SECOND LETTER U C A G THIRD LETTER UUU UCU UAU UGU phe ser tyr cys U UUC UCC UAC UGC phe Ser tyr cys C UUA UCA UAA UGA leu ser (stop) (stop) A UUG UCG UAG UGG leu ser (stop) trp G CUU CCU CAU CGU leu pro his arg U CUC CCC CAC CGC C C A G leu pro his arg CUA CCA CAA CGA leu pro glu arg A CUG CCG CAG CGG leu pro glu arg G AUU ACU AAU AGU ile thr asn ser U AUC ACC AAC AGC ile thr asn ser C AUA ACA AAA AGA ile thr lys arg A AUG ACG AAG AGG (start) met thr lys arg G GUU GCU GAU GGU val ala asp gly U GUC GCC GAC GGC val ala asp gly C GUA GCA GAA GGA val ala glu gly A GUG GCG GAG GGG val ala glu gly G