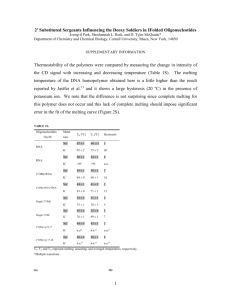
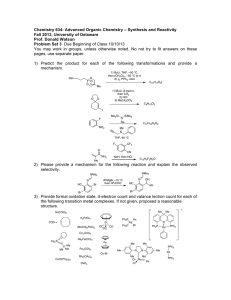
Chemistry 634: Advanced Organic Chemistry – Synthesis and Reactivity
advertisement

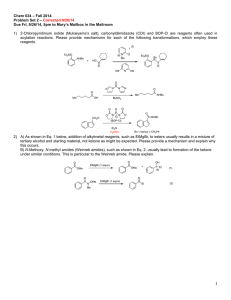
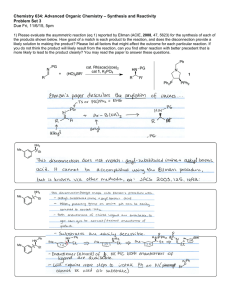
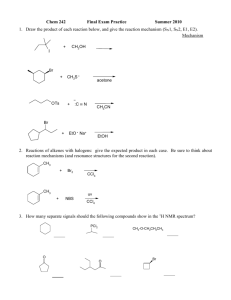
Chemistry 634: Advanced Organic Chemistry – Synthesis and Reactivity Fall 2013, University of Delaware Prof. Donald Watson Problem Set 2 Due Beginning of Class 9/17/13 You may work in groups, unless otherwise noted. No not try to fit answers on these pages, use separate paper. 1) Order the following sets (1 being greatest) and explain why: a) Most electrophilic O O Bu Bu OMe O NMe2 Bu Cl b) Most sterically crowded amine Me Me H2N NH2 Me Me Me NH2 Me Me Me Me NH2 Me Me c) Most acidic (H2O), provide pKa’s for each O O OH O OH Me2N OH F 3C d) Most acidic (DMSO), provide pKa’s for each O O Me Bu Me O Me NBu2 H H OBu H e) Longest expected C=O bond length. O O Bu Bu OMe O NMe2 Bu Cl 2) Predict the products of the following reactions and provide a complete mechanism: Me OH 1) TsCl, pyr 2) NaI, Acetone HO Me Me P(O)Cl3 Et3N O Et SOCl2, pry then NaCN OH HO Me SOCl2, py N NH2 H EMO O PPh3 DEAD OH HO OBn Me Me Me O PhO P N3 PhO OH Me N (DBU) N 3) Provide a mechanism for the following reactions. Be detailed (obey 3-arrow rule). O N Cl O O t-Bu O O OSiEt3 O PPh3, tol, reflux t-Bu Cl O OSiEt3 Cl Cl NaH, THF OSiEt3 OH O Cl OSiEt3 Cl 4) 2-chloropyridinium iodide (Mukaiyama’s salt), carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) and BOP-Cl are other reagents often used in acylation reactions. Please provide mechanisms for each of the following transformations, which employ these reagents. I N Me Et3SiO NHBn + HO Cl Et3SiO Bn N O O Me N Me O N N N N O O Me Me OH O CO2H NHBu BuNH2 O O O P N N O Cl (BOP-Cl) O NHBn Et3N Bn = benzyl = CH2Ph 5) A) As shown in Eq. 1, addition of alkyl-metal reagents, such as EtMgBr, to ester usually results in a mixture of tertiary alcohol and starting material, not ketone as might be expected. Please provide a mechanism and explain why this occurs. B) N-methoxy, N-methyl amides (Weinreb amides), such as shown in Eq. 2, usually lead to the formation of the ketone product under similar conditions. This is particular to the Wienreb amide. Please explain. O O EtMgBr (1 equiv) OMe O OH + OMe Et Et (1) O OMe N Me EtMgBr (1 equiv) Et (2) 6) Predict the equilibrium constant for each of the following reactions. O O OH + Et3N H2O O Li + + LiOH O OMe OMe O Me + N H Me O Me Me Me H N Me Me iPr iPr N Li + O Me Me + Me Me Et3NH + O Li Me + N Li O OK Me Me Li N Me Me Bu Li Me Me iPr N H iPr Me + Me Me + OH Bu H Me 7) Using reactions from the undergraduate curriculum, please provide a retrosynthesis of each molecule that disconnects it to starting materials containing no more that 7carbon atoms and 2-heteroatoms (ie not C or H). O O Me Me OH AcO O NPr2 O hex O Me Me Me 8) Without worrying about the particular reactions needed to accomplish each transformation, please identify retrosynthetic bond disconnections that would results in molecules that do not contain bridged-ring systems. In some cases, there are more than one correct answer, please identify as many as you can. In all cases, there are single step disconnections that can accomplish the task. Me Me O