730 2005 Final exam
advertisement

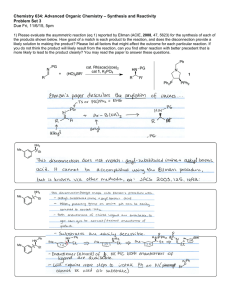
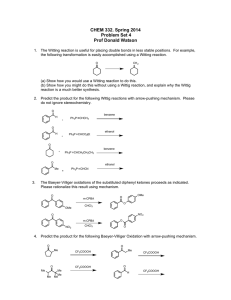
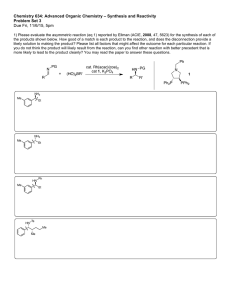
Name………………………………………………………... Chemistry 730 Autumn 2005 Final Examination [December 06, 2005, 11:30-1:30 PM] Total: 120 points Part I 1. (10 points) (a) Define Hammond postulate. Now answer the following questions (be brief, remember: a picture is worth a thousand words!): (b) Use the relative rates of chromic acid oxidation of cis- versus trans- 4-t-butylcyclohexanol to illustrate the Hammond postulate. For full credit, you should show the major conformations of both starting materials, and intermediates, and draw schematic energy/reaction progress diagrams and clearly explain the differences. (c) The relative rates of acid-catalyzed esterification (acetic anhydride + H+) of the two alcohols do not follow the same trend. Why? 1 2. (10 points) The stereoselectivity of enolate formation depends on several factors, including temperature, type of solvent, bulkiness of the base, and size of the R attached to the carbonyl group. Discuss the effect of the solvent/base in the example shown, providing a clear rationale for your answer. O + Z and E enolates base/solvent then TMS-Cl Base/solvent Z:E ratio LDA in THF /23 % HMPA/hexane Li-TMP in THF / hexane 92:8 18:82 (TMP = 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidide) 2 N Li 3. (14 points) Draw the most favorable conformation(s) of the following compounds at room temperature in a nonpolar solvent. ethyl acetate OH CH2(OMe)2 Cl O Me OH Me N H OTs Me OH H H H OH H CO2H H OH cholic acid 4. (6 points) Using transition state models for nucleophilic addition to prochiral carbonyl groups, predict the structures of the major and minor products in the following reactions. Show the model(s). Me O Ph H 1. Me -Ti (OPri)3 2. H3O+/H2O (major) Transition state: 3 (minor) 5. (5 points) Reaction of 4-t-butylcyclohexanone with the chiral amide shown below, followed by quenching with TMS-Cl, gives the TMS-enol ether shown in 88 % ee. Label the hydrogen that is removed in the formation of the major product as pro-R or pro-S. O But 1. OTMS Ph N Li Ph o , THF -90 C 2. TMS-Cl But (88 % ee) 6. (12 points) Rank the following compounds using the criteria suggested: (a) in order of increasing base strength (least basic first): (a) LDA (d) cyclohexanone enolate (Li) (b) n-BuLi (e) NaOMe (c) t-BuLi (f) NaOC(O)CH3 (b) amount of enol content at equilibrium (most amount of enol first): (a) acetaldehyde (e) ethyl acetate (b) cyclohexanone (c) ethyl acetoacetate (d) phenol (c) relative rate of acid-catalyzed H/D exchange of the proton shown in bold (slowest exchange first): (a) CH3C(O)CH2-H (b) CH3C(O)CH2CH3 4 (c) CH3C(O)CH2-But 7. (16 points) (Answer any 4) Illustrate the utility of the following reagents in organic synthesis with ‘real’ examples (no X’s or R’s ). F3C (i) OMe Cl Ph (ii) O But OMe But + – (iv) [Me2N]3S Me3SiF2 (iii) O O O OSiMe3 But 5 (v) + N I– Part 2 8. (22 points) (Answer five. You must answer a, b and c; then choose any two others from d-h). Outline, with solvents, reagents, and approximate reaction conditions, a selective route to each of the following compounds from the indicated starting materials. If you don’t recall the exact conditions, for partial credit, show what strategy you would employ or what is the key disconnection in the synthesis. Me a. H O O O CO2Me OH (absolute configuration shown) • Show the model for stereoselectivity based on the reagent of your choice O OOMe O OMe O OMe OMe b. O O 6 CO2H c. from 1,3-dibromopropane d. OEt O O OBn CHO CHO CH2Ph 7 O O OBn OBn e. O O O O f. Cl (Li-enolate alkylation predominantly leads to elimination; hint: consider the stability of the benzyl cation) g. OEt O O Et O O from O Et Part 3 9. (25 points) Provide the products for the reactions shown below. Suggest a reasonable mechanism (show electron flow or provide a brief explanation) to account for each step, paying attention to stereochemical details. O O N a. a. TiCl4, (i-Pr)2NEt b. PhCH2OCH2Cl O Bn 8 MeS 1. MeO SO2F (methylating agent) 2. KOBut (DME) b. 0 oC to rt O O NH2+ AcO _ O O c. Me Me O H d. H C6H6, 1 h, 65 oC 1. LDA, THF, CD3I 2. KH, THF, CH3I 3. Li/NH3/t-BuOH 9 t-BuMgBr/ether , workup O e. t Bu Na-acetylide/etehr, workup Bonus Question (10 points) Provide a reasonable mechanism (arrow-pushing formalism) for the following transformation. Recall allylsilanes, like allylstannanes we saw in class, are nucleophilic reagents. Ph SiMe3 [PhCH 2 –NH3 ]+ CF 3 CO 2 – + H2 C=O H2 O, 25 oC, 6 h N O OH 10