Severe Weather Structures
advertisement

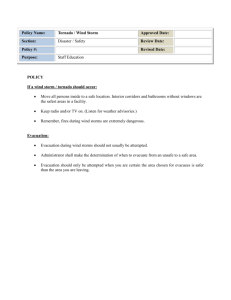
Drexel-SDP GK-12 ACTIVITY Severe Weather Structures Subject Area(s) Science & Technology Associated Unit None Associated Lesson None Activity Title Creating Severe Weather Structures Grade Level 7 (6-8) Time Required 2 hrs Expendable Cost per Group $3 Summary This activity is designed to teach students about various structures used in the civil engineering discipline. The types of structures examined are either built to assist people withstand severe weather events or must withstand severe weather events themselves. Students will conduct research on these structures, create a model of the structure, and present their findings and models to their class. Engineering Connection People must survive when severe weather events such as hurricanes and thunderstorms occur. Likewise, civil engineers must design structures such as bridges and levees to withstand these events so people’s lives are not disrupted. Depending upon the type of structure and geographical region these structures are built to withstand storms that have specific return frequencies. For example, storms that have a 1% chance of occurrence are termed 100-year storms. Highways and bridges may be built to withstand 100-year storms where residential storm drains may be built to withstand 25-year storms. Engineering Category Provides engineering analysis or partial design Keywords Civil Engineer, structure, bridge, culvert, storm drain, storm water retention basin, levee, dam, channel, floodgate Educational Standards • Pennsylvania Science: o 3.2.4 Inquiry and Design Learning Objectives After this lesson, students should be able to: • Define at least one of the studied structures • Understand how civil engineers use weather prediction to design structures Materials List These are suggested materials for each structure although others can be used: • Straws • Clay • Sand • Water • Hot glue gun • Pebbles • Plastic containers • Legos • String/Twine Introduction / Motivation While comparing objects of similar sizes individuals make hypotheses regarding which package contains the greater volume. This lesson was created to demonstrate to students that although packages may no look equivalent they do contain the equal volumes. Vocabulary / Definitions Word Definition Civil Engineer The amount of space enclosed in a space (3-dimensional figure) measured in cubic units. Bridge A structure built to span a valley, road, railroad track, river or other obstacle. Culvert A conduit used to enclose a flowing body of water. Dam A barrier that impounds water or underground streams/ Levee A natural or artificial slope or wall to regulate water levels. Floodgate Adjustable gates used to control water flow in a reservoir, river, stream, or levee systems. Storm Water A storm water management facility installed on, or adjacent to, tributaries Retention Basin of rivers, designed to protect against flooding by storing water for a limited period of time. Channel The physical confine of a river consisting of a bed and banks. 2 Storm Drain A structure designed to drain excess rain and ground water from paved streets, parking lots, sidewalks, and roofs. Procedure This portion can be performed in groups or by individual students 1. Assign students (groups or individually) one of the structures. 2. Ask students to conduct research to sufficiently answer the questions in the attached handout. 3. Provide students with an opportunity to gather their desired materials and build their respective models. 4. Ask students to create a presentation containing the answers to the questions for the rest of the class. Attachments Sever Weather Structures handout. Safety Issues • Use caution with the hot glue gun. It does get hot enough to burn skin. Assessment Post-Activity Assessment Student presentations can serve as assessments of their understanding. Allow the students to ask each other questions about their structures after each presentation. Verify that each of the models contains the major components of the assigned structure. Owner Drexel University GK-12 Program Contributors Quincy Brown, Jonathan Brown, Jason Henderson Copyright Copyright 2009 Drexel University GK12 Program. Reproduction permission is granted for nonprofit educational use 3 Questions For Severe Weather Structure Activity 1) How do you define your structure? 2) Why us your structure important? For example, does it prevent severe weather? Does it help people survive when severe weather occurs? Is it built to withstand severe weather? 3) Provide an example of where you would find your structure. Are there well known examples of your structure? 4) How could you create a model of your structure? What materials would you use? 4