Name Biology Unit 10 Viruses, Bacteria, and Immunity Test Review
advertisement

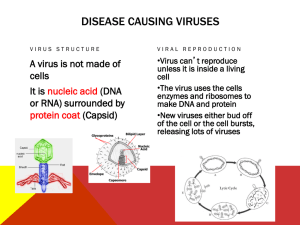
Name ____________________________________Period _________________ Biology Unit 10 Viruses, Bacteria, and Immunity Test Review References: Holt Ch 20 and Ch 40; STEMScopes Viruses Scope, Outreach Notes 1. What is a virus? Pathogens. Segments of nucleic acids contained in a protein coat 2. Why are viruses not considered to be living? Do not grow, no homeostasis, do not metabolize, are not made of cells 3. What characteristics do they share with living things? Contain genetic material, can reproduce (with host cell) 4. What are the parts of a virus? What does each part do? Capsid (protein coat) contains the genetic material (DNA or RNA), most have an envelope (membrane) with glycoproteins that aide in attachment to host cells 5. What is the lytic cycle? Cycle of infection, replication, and cell destruction 6. What is the lysogenic cycle? Virus infects host cells but does not destroy it, instead the viral genome replicates with host cell 7. How can HIV be transmitted? Through bodily fluids 8. How can HIV not be transmitted? Casual contact 9. What cells do HIV viruses attack in the body? Helper T-Cells 10. Name a virus associated with a specific cancer. Hepatitis B, human papilloma virus 11. What are vaccines? How do they work? Immunization. Introduce antigens in a form that will not make a person sick but allows the person to build antibodies 12. Who developed the smallpox vaccine? Edward Jenner 13. Describe the chromosome of a bacterial cell. Single, circular piece of DNA 14. What do eukaryotic cells have that prokaryotic cells don’t have? Cell nucleus and membrane bond organelles, multicellular, linear DNA 15. What are the three bacteria cell shapes? What are the scientific names of the shapes? Coccus, bacillus, spirillum 16. Identify three ways that bacteria are beneficial (helpful) to humans. Digestion, chemical production, environmental purposes 17. How do bacteria reproduce? Binary fission 18. What are flagella? Long hair-like structure that grows out of cell and assists in cell movement 19. What are antibiotics? How do they work? Substance that inhibits or kills microorganisms 20. Who discovered penicillin? Alexander Fleming 21. Why don’t antibiotics work against some bacterial infections? (Hint: what have these bacteria developed that they can pass on to other cells?) Mutations that occur during DNA replication 22. Why don’t antibiotics work for viral infections? Virus not made of cells, antibiotics cannot interfere with cellular processes 23. What is bubonic plague caused by? Bacteria, Yersinia pestis 24. What is cholera caused by? Bacteria, Vibrio cholerae 25. What is the most effective way to prevent the spread of infectious diseases? Washing hands 26. Know if the following are caused by viruses or bacteria: a. HIV- virus b. Influenza- virus c. The common cold- virus d. Anthrax- bacteria e. Botulism- bacteria f. Strep throat- bacteria g. Staph infection- bacteria h. Syphilis- bacteria i. Herpes- virus j. Chicken pox- virus k. Tuberculosis- bacteria l. Hepatitis A, B, C, D, E- virus m. Polio- virus 29. Describe the body’s first line of defense, used to prevent the entrance of pathogens. External barriers of the body, skin and mucous membranes 30. Name three of the body’s nonspecific defenses. Skin, mucous membranes, fever, inflammation, macrophages, ect. 31. Describe how phagocytes fight pathogens. “chew up” invading organisms, release a chem to cause fever 32. Describe the two types of lymphocytes: T-cells and B-cells B-cells recognize specific antigens, T-cells part of system that destroys antigens 33. Which cells release antibodies? What is the function of antibodies? B-cells, specialized proteins that lock onto antigens 34. What is the difference between active and passive immunity? Passive immunity is “borrowed” from someone else 35. Describe how an autoimmune disease affects the body? When immune system attacks own cells