Rivers PowerPoint Presentation
advertisement

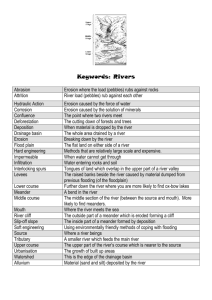
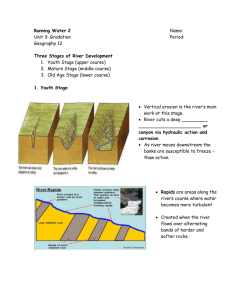
Vincent Raeburn Linlithgow Academy Malcolm McDonald Bathgate Academy Linlithgow A How rivers erode HYDRAULIC ACTION The force of the water weakens and breaks up the rocks ABRASION The material carried in the river wears away the river bed ATTRITION As the pebbles carried by the river crash into each other,they become smaller and rounder SOLUTION The water in the river dissolves the minerals in the rocks How rivers transport Traction Suspension Rolling stones along the river bed.( needs lots of energy) Clay sized particles are carried along by the river flow river flow Saltation Solution Some minerals are dissolved Sand sized particles bounce along the riverbed by the riverwater River Basin Source of River Aye Watershed of River Aye (boundary between basins) Tributary of River Aye Confluence of River Aye and tributary Estuary of River Aye Flood plain Mouth of River Aye Sea Source of river Upper Course Middle Course Lower Course FEATURES OF THE UPPER COURSE V-SHAPED VALLEYS WITH INTERLOCKING SPURS WATERFALLS AND RAPIDS POT HOLES ON RIVER BED Formation of a waterfall Waterfall Retreats upstream Hard rock Soft rock Undercutting The overhang The erodesprocess the Eventually Vertical erosion startsrock again softer collapses Forms plunge pool forming an overhang Steep sides ( gorge ) Eroded rock WATERFALL RETREATS . UPSTREAM . . . OVERHANG UNDERCUTTING OF SOFT ROCK PLUNGE POOL The River Avon has smoothed off parts of this hard igneous rock. . . What is this process called? MEANDERS Meanders Possible break through point Most erosion on the outside of the bend .. Fastest flow Possible ox-bow lake Flood plain © Used with the permission of the Geological Survey of Canada, Natural Resources Canada Available at http://sts.gsc.nrcan.gc.ca – Terrain Science Division River bend Fastest current slowest current Bank will collapse Small river cliff Outer bank Is undercut Deepest part of the river Slip off slope ( river beach ) Deposition of Sand and shingle Formation of an ox-bow lake The Some river Eventually now follows during the a period new route ofMost erosion bends get closer Theheavy meanders change shapethrough river flow it cuts and closer Most deposition through time Small river (Slip off slope) cliff is formed © Used with the permission of the Geological Survey of Canada, Natural Resources Canada Available at http://sts.gsc.nrcan.gc.ca – Terrain Science Division The bends migrate At the bends the Sideways leaving river flows faster The neck gets narrower The old meander deposits on the inside at the outside The erosion the andasnarrower Is left a small lake Of the makes bend Meanders more pronounced (OX - BOW lake) Want to see that again ? NARROW MEANDER NECK FUTURE OX-BOW LAKE Gentle valley sides River is actually flowing above The floodplain !! Flat floodplain Layers of silt Deposited during floods Levees is often artificially strengthened Coarse material Forms natural levees Characteristics Middle Course Lower Course quite steep quite wide gentle wide shallow quite deep deep Straightness winding Load little meandering Type of load large/small angular medium/small rounded Slope Width Depth Main work Valley width Upper Course usually steep narrow some big meanders lots small+ rounded erosion Transportation transportation transportation deposition narrow quite wide wide tributaries V shaped valley Steep Valley sides meander ox-bow lake Flood plain Reproduced with kind permission of Ordnance Survey © Crown Copyright NC/03/18990